5 Best Ransomware Protection Tips to Protect Your Organization
What is the best ransomware protection for your business? Is there truly a “best way” to protect against ransomware?
In a way, ransomware is a lot like kidnapping. An attack locks down critical systems and files to hold data hostage. A cyber criminal demands a ransom, much like a kidnapper would try to extort money, in exchange for the victim to regain access to their data and resume operations. Most of the time, it takes just a moment of employee negligence, procrastination, or even just them engaging with the wrong email link or attachment to weaken an organization’s cyber security posture.
The global damages of ransomware were estimated at $11.5 billion by the end of 2019.
So, how can you protect yourself from ransomware?
The good news is that you don’t need to spend millions on protecting your organization from ransomware attacks. In this article, we discuss five free (or at least inexpensive) ways to protect against ransomware attacks.
Best Ransomware Protection Method 1: Deploy a Robust Backup System
Backups are the best way to defend yourself or your business against ransomware in terms of getting up and running after an attack.
In May 2019, a hacker shut down Baltimore’s major city government servers and online facilities. They demanded a $76,000 ransom to restart the entire system. The city’s leadership took the high road and refused to pay. Unfortunately, however, they didn’t have a backup of most of their data. As a result, it cost them $18.2 million to restore the system on their own!
In most ransomware cases, the victims suffer substantial financial losses because they don’t have proper backups of important data. Otherwise, they would be able to easily restore all the data and resume to daily work within minutes or hours, depending on the amount of data they would need to restore.
You can’t rely on your hosting site’s backups. They store data on servers, which is the same location where your original data is stored. So, when an attacker gets access to the original data, it means they will, by default, get access to your backup files, too!
This is why it’s so important to use a product like CodeGuard to protect your backup data on a separate third-party cloud platform. The most effective backups are those that are automatic, encrypted, and offer restoration functionality directly from the cloud platform’s dashboard.
Best Ransomware Protection Method 2: Increase Your Email Security Through Best Practices and Training
One of the most popular methods of spreading ransomware is via email. This is why cyber awareness training and teaching your employees email security best practices is essential.
Teach Cyber Awareness
Teach your employees how to differentiate a genuine email from a fake one. This includes helping them learn to identify common phishing email characteristics and educating them to not open any links or attachments in suspicious emails. Inform them to only download attachments in emails from people whose identities they’re 100% confident about. And let them know to always scan the attachment using a reliable malware/anti-virus scan before downloading it.
Help Them Learn to Read and Understand Email Headers
Another best practice for employees to remember is to always check the sender’s email address. Genuine companies typically send emails from their official email addresses with their domain name included in it. (For example, [email protected]).
Check out the following example of two phishing emails I received recently. They both crafted to look like they’re from the Apple Store. They used “App Store” and “Apple Store” as the display names. But when you check the senders’ email addresses, you can clearly differentiate the fake one from the genuine one.
Ensure Macros Are Disabled
Don’t enable macros in email attachments. Once you run the macro, the malware will take control of the device’s operating system and all the data. The good news? Recent versions of Microsoft Office disables macros by default. This means that, in many cases, users would have to manually turn on macros in order for the macros to run.
Best Ransomware Protection Method 3: Download Only from Trusted, Reputable Sources
Always be highly cautious while downloading anything from the internet. As soon as you download a malicious program, the malware executes on your system and does whatever it was programmed to do.
Download software from well-known websites, vendors, and publishers. Also be sure to check the user reviews, if available.
Take extra precautions when you’re downloading anything that’s free of cost. The internet is flooded with free games, antivirus programs, digital certificates, plugins, themes, templates, apps, songs, movies, books, TV series, and more. Sometimes, attackers create fake free software programs and apps to lure potential victims.
Train your employees to recognize the signs of a legitimate site.
Best Ransomware Protection Method 4: Perform Regular Updates to Keep Systems and Programs Up to Date
Regularly update all software, operating systems, devices, themes, plugins, and apps. Updates are there for a good reason. Generally, software publishers find vulnerabilities in old versions of their software, fix them, and release new versions, updates, or patches.
Attackers are always in search of such vulnerabilities — they just need to know the vulnerable areas of old software and the people who are still using them to exploit them! So, if you don’t update your system as soon as a new update is released, attackers can easily exploit the weaknesses of the old version. So, always be methodical about implementing updates.
Best Ransomware Protection Method 5: Restrict Employee Access
Employees have access to the most sensitive data of the companies at their fingertips. In many ransomware cases, attackers use targeted employees’ stolen login credentials to access databases and systems that store sensitive information. In other cases, employees themselves steal and encrypt their companies’ data or give access to their systems to outside attackers in exchange for money.
Take Asurion’s ransomware situation as an example. In August 2019, Asurion, a leading phone insurance and tech support company, was hit by an insider threat ransomware attack in which its own former employee Nicholas Burks stole 100 terabytes (TB) of sensitive information. As a result, Asurion paid a $300,000 ransom.
Such examples show that companies must restrict employee’s access to the bulk data. Employees can have access to just the small piece of data which they need at the time of performing their job duties. As soon as their work is over, the data must be encrypted and stored safely.
Final Words on Ransomware Protection
In today’s digital era, organizations are frequently crippled, and employees are unable to perform their daily tasks if they don’t have access to necessary data — even for a short period of time. Attackers know this fact well, and that’s why the ransomware attacks are not going away any time soon.
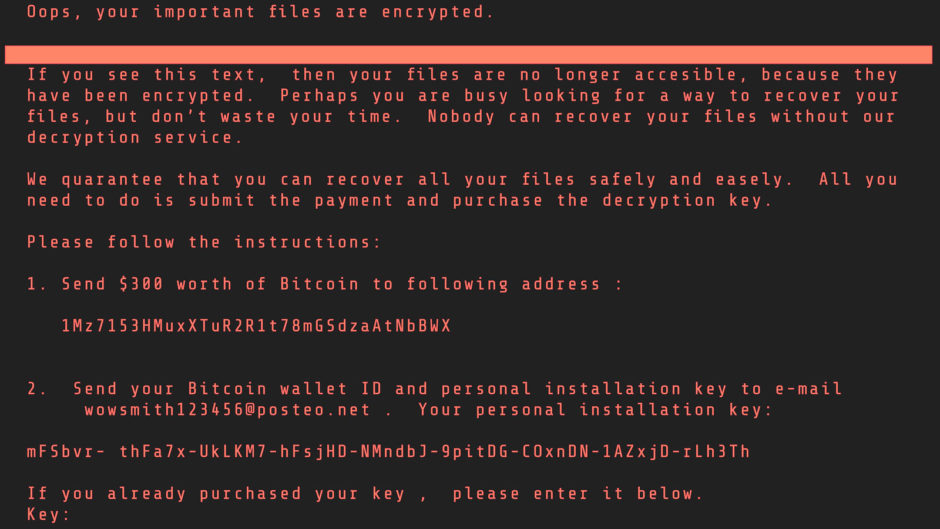
You must take all the precautions to protect your data. But in an unfortunate event of a ransom attack, the best policy is not to pay the ransom. Even if it looks the easiest way to get out of the situation, it might prove even more dangerous in the long run. There’s no guarantee that the hacker will restore your access to the data even if you do pay the ransom. Plus, once you pay, the other attackers will consider your organization a “soft target” and feel encouraged to target it for future cyber crimes.
If necessary, don’t hesitate to take the help of your local police department or even the FBI. Most states have a special department for cyber crimes. As we said earlier, the best way to protect against ransomware is to create backups on a third-party cloud platform. You should also know that there are some paid and free ransomware decryption software tools available in the market these days.




















 (17 votes, average: 4.41 out of 5)
(17 votes, average: 4.41 out of 5)






No comments