What Is a Private Key? A 90-Second Look at Secret Keys in Cybersecurity
In a world where cyber attacks increase 50% year over year, your data need security, and security need private keys. Explore what a secret key is and its role in protecting your organization & data
Passwordless authentication, digital certificates, and encryption are all examples of how you can improve your organization’s cyber security. What do they have in common? Their reliance on a secret tool known as a cryptographic private key.
Find out in a flash what a private key is and how it aids your cybersecurity. Ready? Start the clock.
What Is a Private Key? A Quick Definition of a Private Key
A private key is a secret, randomly generated string of alphanumeric characters that’s used to secure data and assert your verifiable identity online. (I.e., it proves your identity and keeps your data secure.) How? By creating digital signatures and encrypting and/or decrypting data.
A private key:
- Must be kept secret, meaning that no one but you should have access to it.
- Is used in asymmetric or public key encryption (more on that in a sec).
- Is used to carry out symmetric encryption (i.e., encrypting and decrypting data using the same key).
Here’s a quick look at how it works:
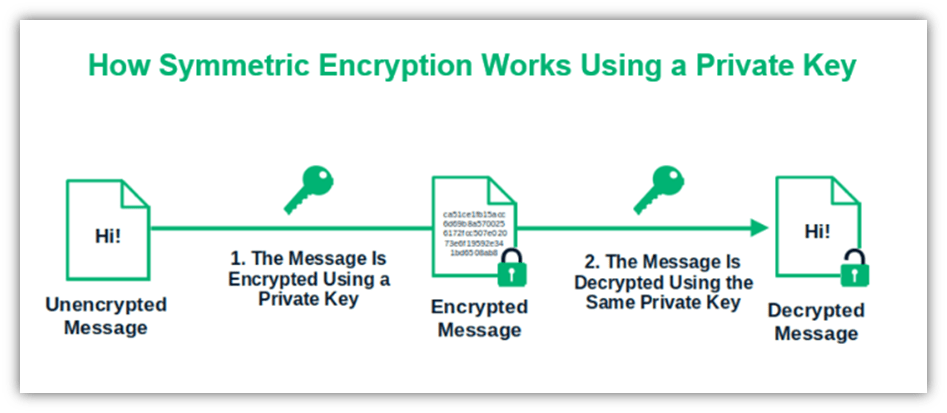
Image caption: The graphic shows an example of symmetric encryption with a shared secret key that both parties know
A Private Key Is Related to a Public Key (But Is Mathematically Different)
A secret key is half of a what’s known as a public-private key pair. The other half, as you may have guessed, in the public key. But how are these two keys different? A public key:
- Is publicly known, meaning that anyone can access it because it’s not a secret.
- Is used in asymmetric encryption (i.e., data is encrypted using a public key and decrypted using a private key)
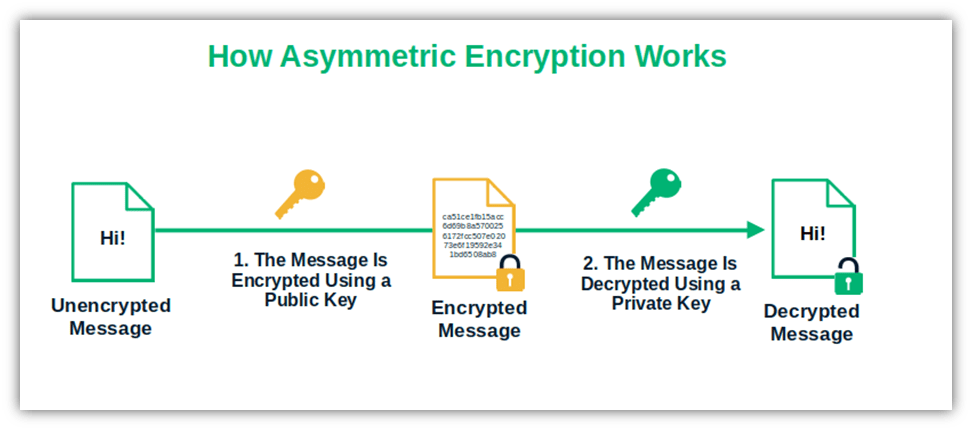
Image caption: This is how asymmetric encryption works. The data are encrypted using a public key and decrypted using a private key.
A Secret Key Is Only as Effective If You Keep It Secure
Okay, this part is really important:
- The security of a private key is directly proportional to its length and complexity.
- You must keep the key secure. This entails carefully managing and storing your secret keys to keep them out of the hands of unauthorized users (e.g., cybercriminals).

Image caption: The graphic shows a few examples of private key sizes. The bigger the key is, the higher its level of security.
What Is the Role of Private Keys in Cybersecurity?
A private key helps you:
- Encrypt and/or decrypt data
- Assert your digital identity
- Protect the integrity of your data
Encrypt and/or Decrypt Data to Keep It Secure
This protects the data and files you send and/or receive via the Internet, which helps to protect it against access by unauthorized users (such as via man-in-the-middle attacks). Here’s how:
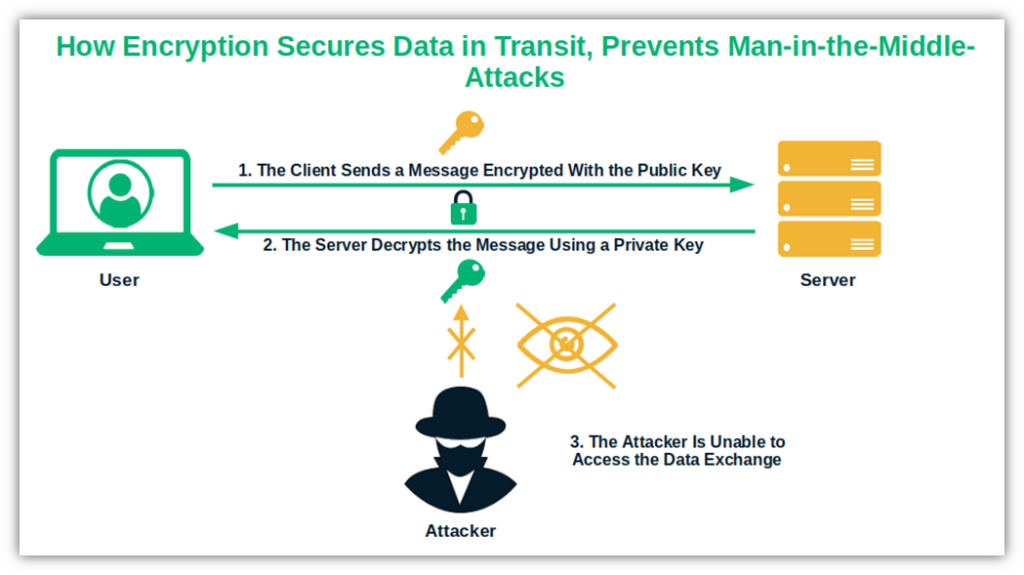
Image caption: With a private key, you can decrypt an encrypted email message.
Assert Your Digital Identity in a Verifiable Way (Proving Your Identity)
You can add your digital identity to website connections, software, files, emails, and other digital assets. It helps recipients and users know they’re talking to the right party and using legitimate websites or software.
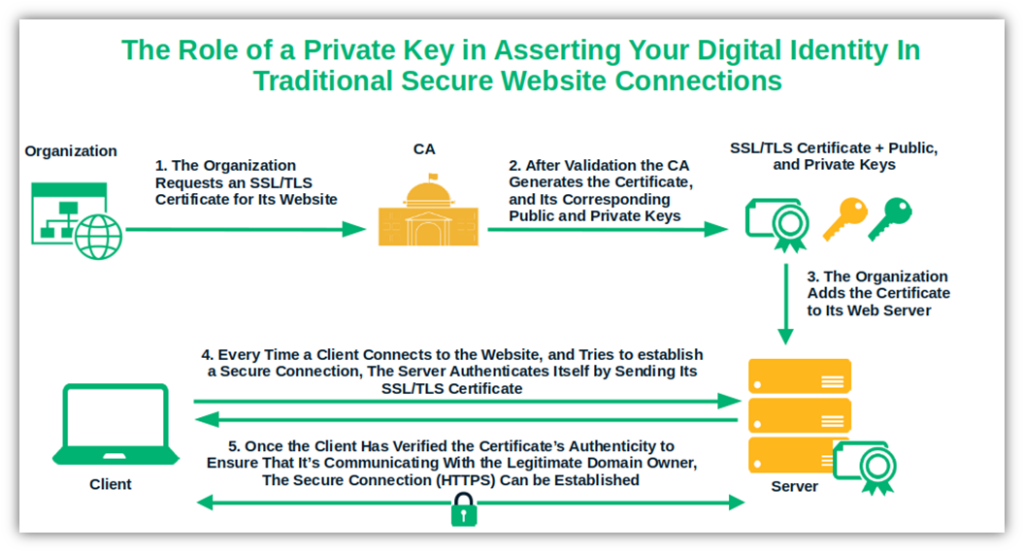
Image caption: The graphic shows the utilization of a secret key in establishing an HTTPS secure connection.
Protect Data Integrity Using Cryptographic Functions
Your private key plays a crucial role (along with hashing) in protecting the integrity of your data. For example, code signing enables you to prove to your customers that your published software is authentic and hasn’t been tampered with since your organization signed it.
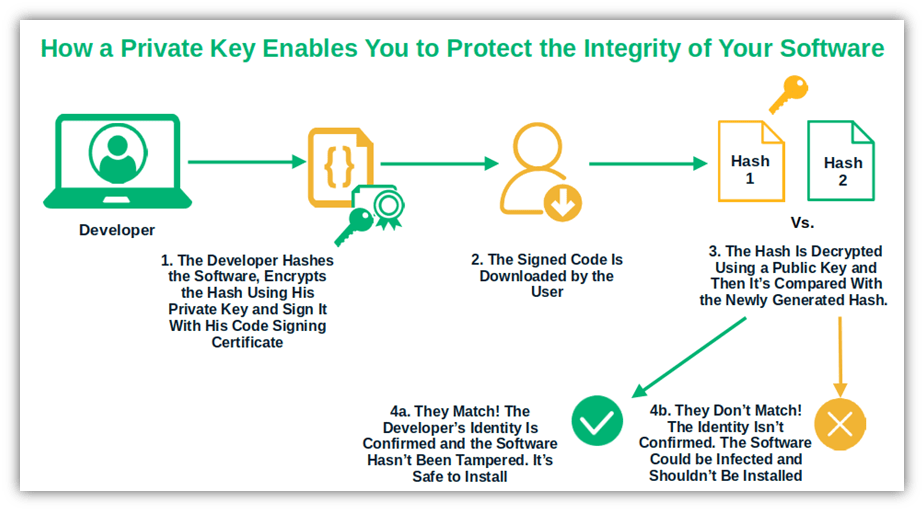
Image caption: The graphic shows how a secret key enables you to sign your code and assert your digital identity to keep your organization and customers safe when publishing software. Paired with a cryptographic hash function, it helps play a role in protecting the integrity of your software.
Want to know more about private keys? Check out this great video:
Final Thoughts on Private Keys in Cybersecurity
It’s clear to see why the private key is a critical part of cybersecurity. In the era of near-instantaneous digital communications, this secret tool enables you to:
- Move toward a zero-trust architecture,
- Assert your identity to increase customer trust,
- Keep your organization’s assets and customers’ data secure from compromise,
- Minimize the risks of attacks
That’s not bad for just a small little key, right?




















2018 Top 100 Ecommerce Retailers Benchmark Study
in Web Security5 Ridiculous (But Real) Reasons IoT Security is Critical
in IoTComodo CA is now Sectigo: FAQs
in SectigoStore8 Crucial Tips To Secure Your WordPress Website
in WordPress SecurityWhat is Always on SSL (AOSSL) and Why Do All Websites Need It?
in Encryption Web SecurityHow to Install SSL Certificates on WordPress: The Ultimate Migration Guide
in Encryption Web Security WordPress SecurityThe 7 Biggest Data Breaches of All Time
in Web SecurityHashing vs Encryption — The Big Players of the Cyber Security World
in EncryptionHow to Tell If a Website is Legit in 10 Easy Steps
in Web SecurityWhat Is OWASP? What Are the OWASP Top 10 Vulnerabilities?
in Web Security