A Guide to PKI Authentication with 8 Examples
$900 million and counting — that’s the price the UnitedHealth Group is paying for a data breach and ransomware attack caused by weak authentication practices. PKI certificate-based authentication isn’t new, but it adds a layer of protection. Here’s how…
Each day, headlines are filled with a steady stream of ugly and scary reports about malicious websites, malware-infected software, and phishing email scams. So, who or what can you trust online?
Public key infrastructure (PKI) authentication helps you answer this crucial question. It empowers you to prove to your customers what’s true and earn trust in a world where digital identity, data integrity, and authenticity are always in question.
Are you ready to learn more about PKI authentication and discover how it can assist you in winning the battle between trust and deception? Let’s get the ball rolling.
What Is PKI Authentication?
PKI-based authentication is a set of processes, tools, and policies designed to secure online communications by enabling one or both parties to verify the entity on the other end of a connection. But PKI-based logins do more than that.
When implemented properly, PKI-based authentication leverages digital certificates and cryptographic key pairs (more on that momentarily) to validate that an entity (i.e., a user, server, or device) really is who or what they claim to be. For example, it lets you securely access virtual private networks (VPNs) and Wi-Fi. It also confirms your identity when you digitally sign documents, code, and emails.
It’s a fundamental step for a secure online interaction that answers the question: “Who are you?”
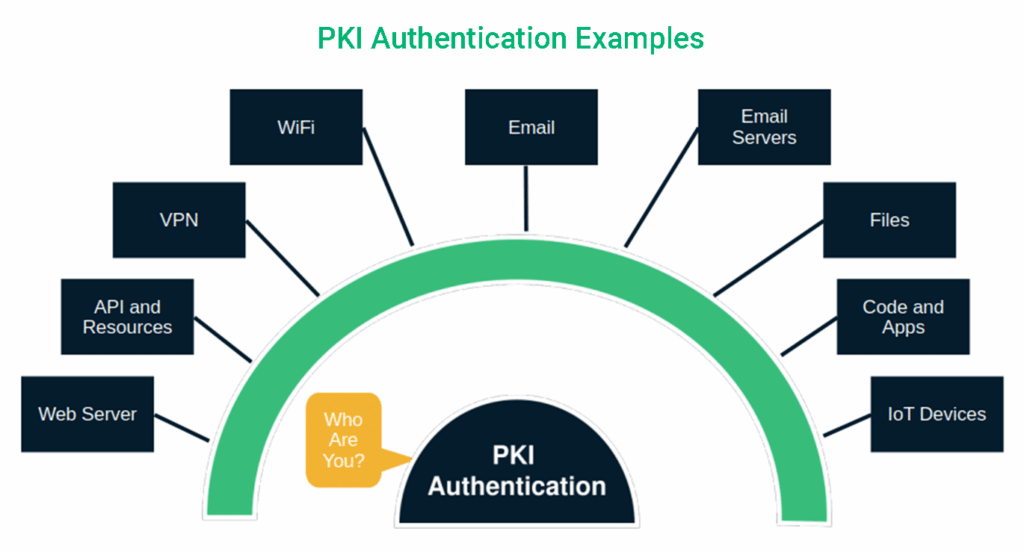
8 PKI-Based Authentication Examples You Can Use Within Your Organization
PKI authentication is like coffee. It’s so versatile that you can find it everywhere — from online banking and emails to the smart devices in your office. And guess what? If you own a smart coffee maker, it’s in that, too. Let’s look at a few examples of how you can use certificate-based authentication within your business.
1. PKI Authentication for Websites
Imagine a customer wants to place an order on your online shop but hesitates to enter their credit card details and personal information. Why? Because the user doesn’t know who’s really behind your online shop and is scared by the “this connection is not secure” message they’re seeing on your site.
PKI authentication helps you solve this problem, providing assurance that you’re really you. It allows your customer’s web browser to authenticate your server before establishing the connection. This way, the user can be sure they’re visiting a legitimate website.
To be as certain as possible, the customer can manually verify the organization information included in your secure socket layer/transport layer security (SSL/TLS) certificate that’s used for PKI authentication. Just as shown in the example below:
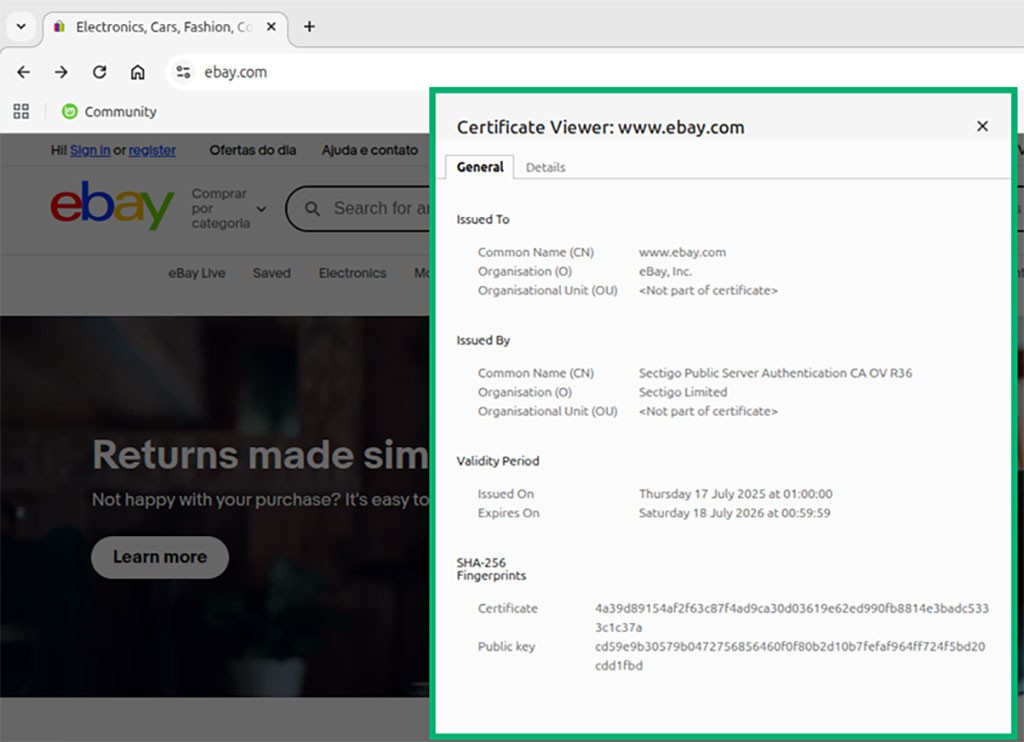
2. Robust PKI Authentication for Your Sensitive APIs and Resources
Application programming interfaces (APIs) are the glue that allows systems and applications to communicate and transfer data smoothly. Development teams use them to streamline workflows and deliver software faster. As you can imagine, this makes APIs juicy targets for cybercriminals.
Akamai’s latest State of Apps and API Security report underscores these concerns. Based on the investigation, cybersecurity incidents related to one or more issues listed in the Open Worldwide Application Security Project (OWASP) API Security Top 10 rose by a whopping 32% year over year in 2024.
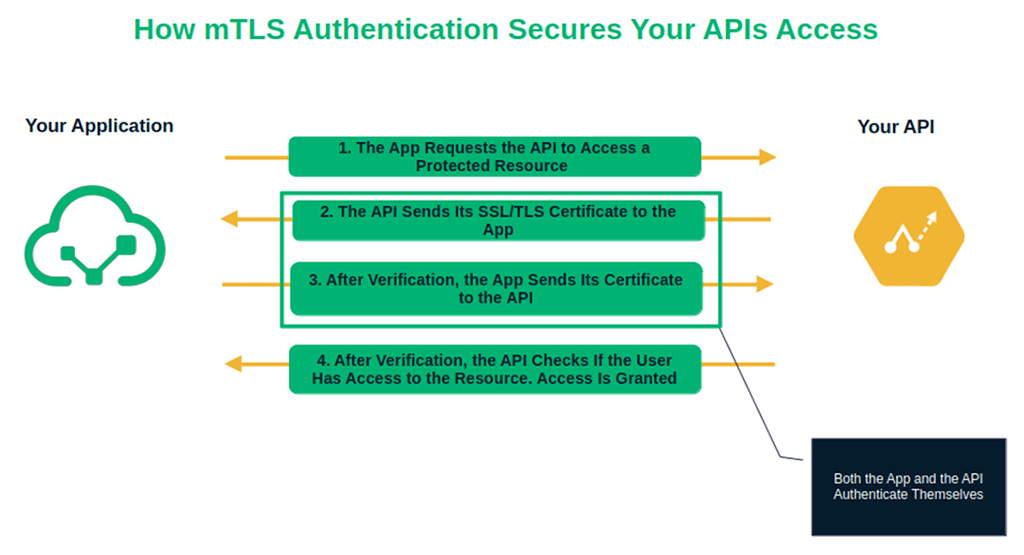
Here’s where mutual authentication in TLS (mTLS) comes in. This more robust type of PKI authentication includes a twist that further secures your APIs and other sensitive resources.
How? When your application requests access to an API protected by PKI authentication with mTLS, the API presents its SSL/TLS certificate. But that’s not enough. The application also proves its identity by sending the certificate to the API. Only then will the app (and consequently the user) get access to the protected resource.
OK. That’s an extra step compared to the classic PKI authentication method we’ve just seen. However, several organizations use it. Take Mastercard, for example. Their API harnesses the high level of security offered by mTLS to restrict access to sensitive resources to authorized users only.
3. PKI-Based Login for a Virtual Private Network (VPN)

A VPN allows you to securely connect to a network, masking your IP address and using advanced encryption to secure data in transit. It protects you from man-in-the-middle (MITM) attacks and snoopers aiming to steal the information you exchange over the internet. But what it can’t do is protect your credentials against phishing and malware-based threats.
PKI authentication can. It replaces your ID and password with a secure digital certificate issued by your company, or a trusted certificate authority (CA) and vendor such as SectigoStore.com. No more credentials, no more bad guys trying to steal your username and password.
That’s fantastic news, given that the Specops research team discovered over 2 million VPN passwords that were stolen via malware in just one year.
4. PKI Authentication for Secure Wi-Fi Access
In 2023, hackers destroyed a 158-year-old transport business by exploiting one weak password. They guessed an employee’s credentials, encrypted all the company’s data, locked the systems, and asked for a hefty ransom. Since the company didn’t have the money, it ultimately went under.
Yup. Non-PKI-based authentication can really get your organization into trouble sometimes. Suppose that you implement PKI authentication for Wi-Fi access. Your users can connect to your company’s wireless network without a password. Cause removed, end of the problem. And if you’re worried about cybercriminals stealing their certificate’s private key, fear not. They’re all safely stored on their devices’ trusted platform modules (TPMs) and are inaccessible to device users.
5. PKI Authentication for Emails and Email Servers
The last quarter of the year is always an exciting time for everyone, especially for businesses and, surely, hackers. Cyber Monday, Black Friday, Christmas. Like the song says, “it’s the season to be jolly!”
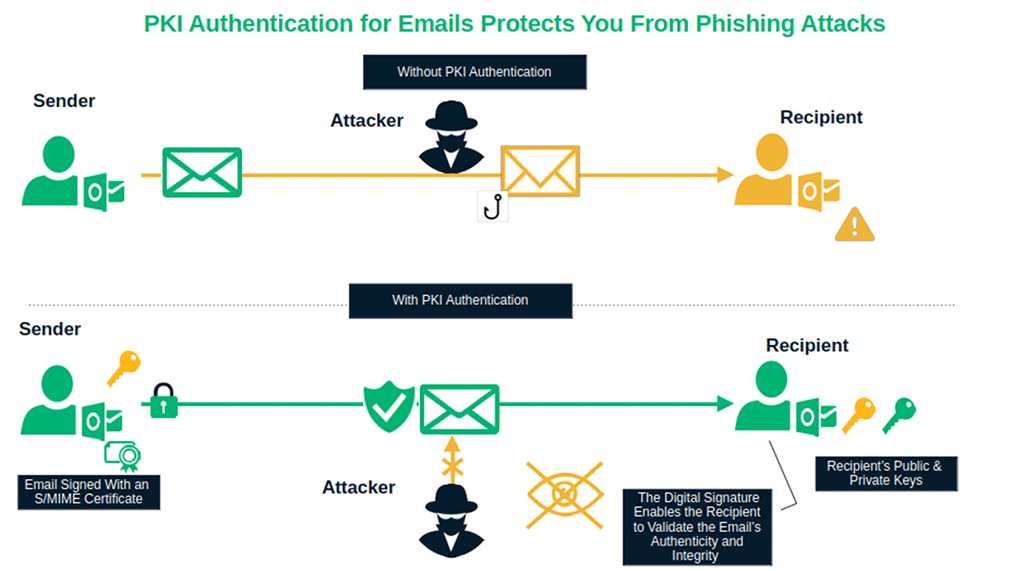
PKI authentication is your best defense against phishing and email scams that could otherwise do lasting damage to your company’s reputation. When you send your emails and newsletters signed with a secure/multipurpose internet mail extensions S/MIME certificate, PKI binds your verified digital identity to the message.
That means your customers and employees will always feel confident that the messages you send them are coming from else but you. That’s a game-changer considering that Pew Research reports that 63% of American adults receive scam emails at least weekly. (28% indicated they receive these messages daily.)
Do you want to feel even more secure and comply with Google’s latest email security and authentication requirements for email senders? Install an SSL/TLS trusted certificate on your email server to enable public key infrastructure authentication. It’ll help you to:
- Secure your emails in transit between the email client and the server.
- Increase the chances your messages will be successfully delivered to your recipients’ inboxes.
- Minimize the risks of Gmail flagging your emails as spam, blocking them, or even temporarily reducing your sending rate limits.
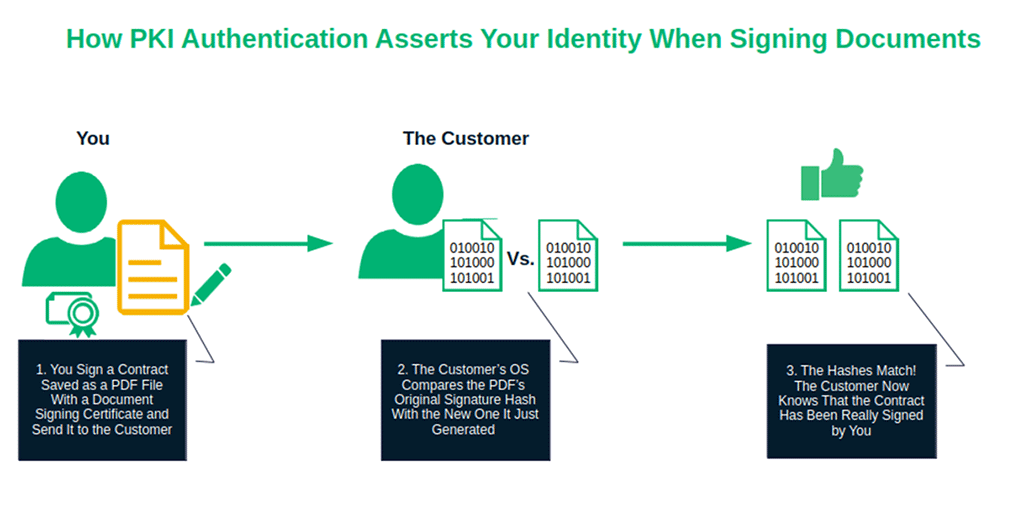
6. PKI Authentication for MSO and PDF files
Did you acquire a new client and want to send them a binding contract or some legal documents via email? Let’s ensure that the attachments won’t be tampered with and that the client will know immediately that they’re coming from you (and not an imposter).
It’ll show your client that you’re taking security seriously and that you’re a partner he can trust. That’s especially fundamental when you consider that Check Point reports over 22% of malicious email attachments were delivered through PDF in 2024..
So, purchase a Sectigo document signing certificate and use it to sign your Microsoft Office (MSO) files and/or PDFs. PKI authentication will assert your identity through the cryptographic digital signature you’ve just applied.
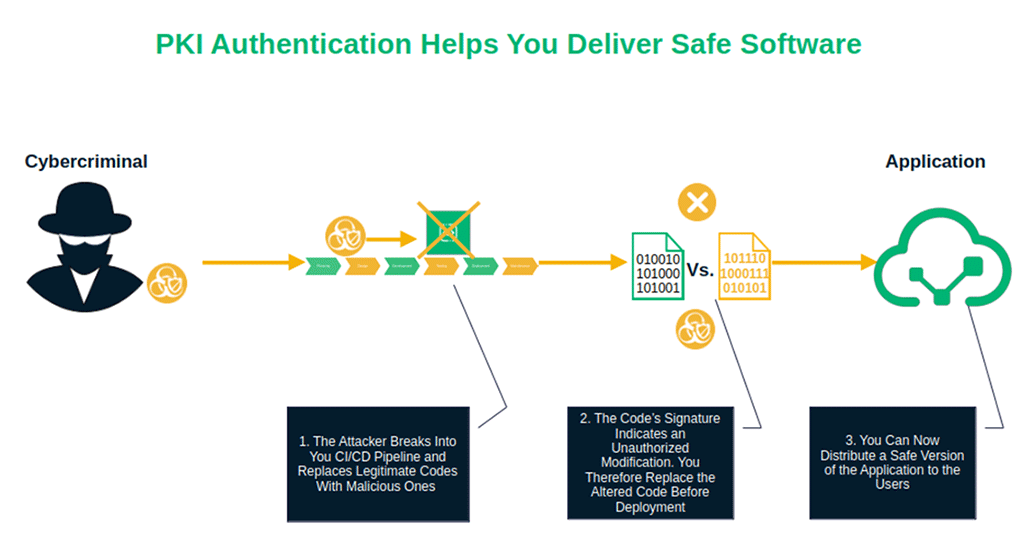
7. PKI Authentication for Code, Scripts, and Applications
Software publishers invest significant money, time, and resources into software development. But it’s all for nothing if the code or scripts aren’t adequately protected.
A code signing certificate, combined with PKI authentication, lets your users’ operating system confirm your identity and the integrity of the code in one go. Meaning, they’ll know it was signed by your private key and that no one has tampered with it since.
But that’s not all, folks. PKI authentication also works its magic when you digitally sign:
- Software artifacts. It shields your continuous integration/continuous deployment (CI/CD) pipeline from malicious code modifications. This way, you deploy to production only trusted and authenticated components.
- Software updates. This action shields your software supply chain from potentially disastrous malware infections.
- Software bills of material (SBOMs). Signing the list of all the components used to create the application boosts customers’ confidence in your products.
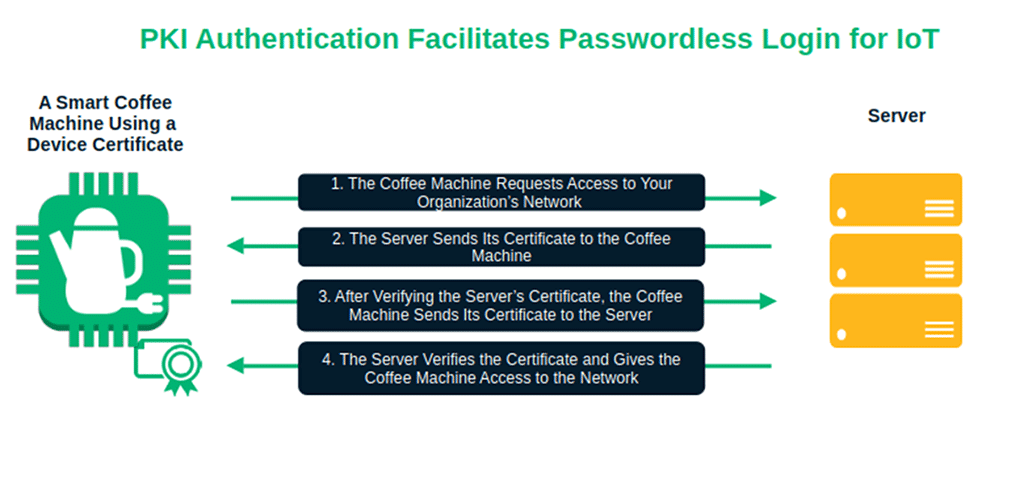
8. PKI Authentication for IoT Devices
Isn’t it great when you walk into the office and the lights turn on automatically? Or when a sensor alerts you about a potential breakdown of a machine weeks before it occurs? IoT devices have made our lives easier and more convenient. Nevertheless, they’ve also dramatically increased the risk of data breaches.
In 2025, over 1 million IoT-based medical devices were compromised, leaking sensitive patients’ sensitive data. On top of it, that year, the BadBox 2.0 botnet infected over 10 million IoT devices. PKI authentication may not be a cure-all. However, it’ll help you secure your IoT connections.
A digital device certificate enables your IoT device to authenticate to your network without requiring a password that could otherwise be compromised. It also protects the data exchanged between devices and cloud services with strong encryption.
Why Should You Implement PKI Authentication?
In 2024, the telecom giant AT&T was a victim of two massive data breaches that exposed the sensitive personal information of millions of customers. The company now faces a whopping $177 million settlement.
If this isn’t a good enough reason to strengthen your organization’s security by implementing PKI authentication, let me provide you with a few more. PKI authentication:
- Enhances communication security. When you use PKI, end-to-end encryption protects all your data transmissions. That makes it more challenging for bad guys to steal sensitive information through GenAI or conventional MitM attacks.
- It also lets you streamline the access and control processes. Say goodbye to complex passwords and clunky access. You can now enjoy faster, more secure logins.
- Offers scalable security. It doesn’t matter if you need to authenticate a few or millions of devices, users, and assets. Organizations of any size can easily deploy PKI-based logins.
- Facilitates compliance. Achieving compliance with privacy and security regulations can be challenging. PKI authentication puts you on the right track.
- Ensures non-repudiation. When you digitally sign emails and documents, the PKI authentication process provides irrefutable proof that you signed them.
- Boosts trust. Public key infrastructure authentication proves to customers and partners that you’re serious about security and data protection. Digital certificates, PKI-based logins, and encryption protect online transactions and minimize the risk of attacks.
Public Key Infrastructure Authentication. Here’s How It Works at a Glance
Every time I think about the PKI authentication process, it reminds me of the tradition of exchanging business cards in Japan. While in many countries business cards are just a formality, nearly out of fashion, in Japan, the meishi koukan (i.e., a business card exchange) is almost a ritual that can make or break a potential business relationship. The process follows precise steps, much like PKI authentication.
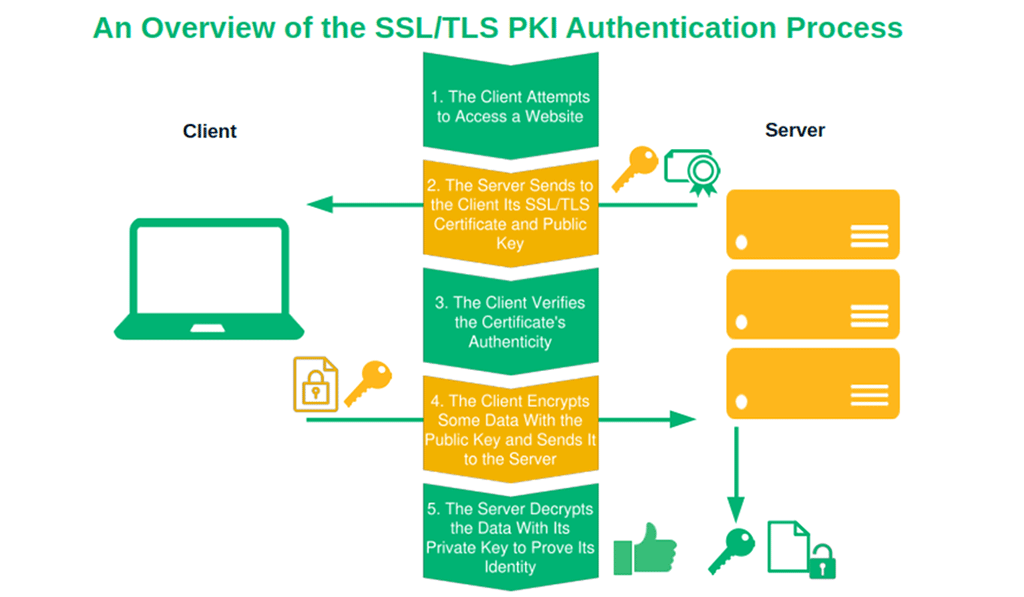
So, how does PKI authentication work? Let’s say your organization has just installed an SSL/TLS certificate on your website. Here’s what happens during the authentication phase of a traditional TLS handshake when, for example, a customer visits your website.
Step #1: The Connection Request
When the customer opens the browser and types your website’s URL, the client requests to establish a secure connection.
Step #2: Sharing the Certificate
The web server sends the client its SSL/TLS certificate and the related public key. Like all publicly trusted X.509 digital certificates (e.g., S/MIME, code and document signing), it was signed by the issuing CA and includes all information about your organization.
Step #3: Certificate Verification
The client uses the chain of trust to verify whether your SSL/TLS certificate was issued by a trusted CA. It does this by tracing your digital certificate to the CA that issued it through a series of digitally signed certificates (i.e., root, intermediate, and leaf). If everything goes well, this is the first proof that the client communicates with the correct server.
Step #4: Public Key Encryption
To finally confirm the server’s identity, the client uses the server’s public key to encrypt a set of data. It then sends it to the server (which has to have the corresponding private key for the next step).
Step #5: Private Key Decryption
We’ve reached the last PKI authentication step. The server attempts to decrypt the data with its private key. If the operation succeeds, it confirms that the identity of the server is what it claims to be. Check. PKI authentication completed.
Afterward, the clients and the server will establish an encrypted session to keep the data exchanged private. But what if you chose to implement the more robust mTLS PKI authentication we mentioned in one of our examples above?
In that case, the process requires the client to prove its identity, too. Therefore, after the client has validated the server’s identity, it also sends its own client authentication certificate to the server. Only after the server has authenticated the client will the encrypted connection be established.
Do you want to know more about how PKI works? Don’t miss our PKI article series:
- The inner workings of public key infrastructure
- Demystifying PKI Technology: An Essential Guide for IT Security Professionals
- PKI 101: All the PKI Basics You Need to Know in 180 Seconds
Final Thoughts on PKI Authentication With 8 Examples
Protecting your organization and preventing your customers’ sensitive data from falling prey to aggressive attackers is now harder than ever. Unprecedented technological advancements, such as AI tools, are making cyber threats increasingly challenging to fight.
Thankfully, PKI authentication can help. Certificate-based authentication can transform your websites, network, and systems into digital trustworthy islands where everything is verifiable, authentic, and compliant. So, get your digital certificates and start building security and trust. Don’t forget, though. For PKI authentication to work its magic, you’ll also need a proper certificate and key management lifecycle strategy. But that’s what Sectigo Certificate Manager is here for, right?





















2018 Top 100 Ecommerce Retailers Benchmark Study
in Web Security5 Ridiculous (But Real) Reasons IoT Security is Critical
in IoTComodo CA is now Sectigo: FAQs
in SectigoStore8 Crucial Tips To Secure Your WordPress Website
in WordPress SecurityWhat is Always on SSL (AOSSL) and Why Do All Websites Need It?
in Encryption Web SecurityHow to Install SSL Certificates on WordPress: The Ultimate Migration Guide
in Encryption Web Security WordPress SecurityThe 7 Biggest Data Breaches of All Time
in Web SecurityHashing vs Encryption — The Big Players of the Cyber Security World
in EncryptionHow to Tell If a Website is Legit in 10 Easy Steps
in Web SecurityWhat Is OWASP? What Are the OWASP Top 10 Vulnerabilities?
in Web Security