6 Real-World SMB Cyber Security Threats That Will Keep You Up at Night
Does the thought that cyber attacks are five times more likely than fire to harm your business send shivers down your spine? You’ve seen nothing yet. Discover six terrifying real-life examples of SMB cyber security threats and 11 tips to stop them
JumpCloud reports that 84% of the IT professionals at small and medium enterprises (SMEs) polled in Q3 2024 say they’re worried about the security of applications and resources managed outside of IT (i.e., shadow IT).
However, while shadow IT has been identified by the organizations interviewed as the root cause of 37% of data breaches experienced in 2024, it isn’t the only monster disrupting small business (SMB) owners’ sleep.
In this article, we’ll explore six real-life examples of cyber security threats that are likely to keep SMB leaders up at night. Discover a few tips that’ll help you end your sleepless nights.
Top 6 SMB Cyber Security Threats That’ll Get Your Heart Racing
What are SMBs thinking when they’re lying in their beds in the dim light of the moon? What’s keeping them awake besides the neighbor’s cat meowing loudly? It’s time to find out with this list of cyber security threats.
Cyber Security Threat #1: Ransomware Attacks
Ransomware is a type of malware that, once unleashed, locks you out of your system and/or files until you pay the attacker big bucks. In some cases, the attacker will exfiltrate your data to servers they control so they can either demand a second ransom or leak/sell your data later (to your detriment).
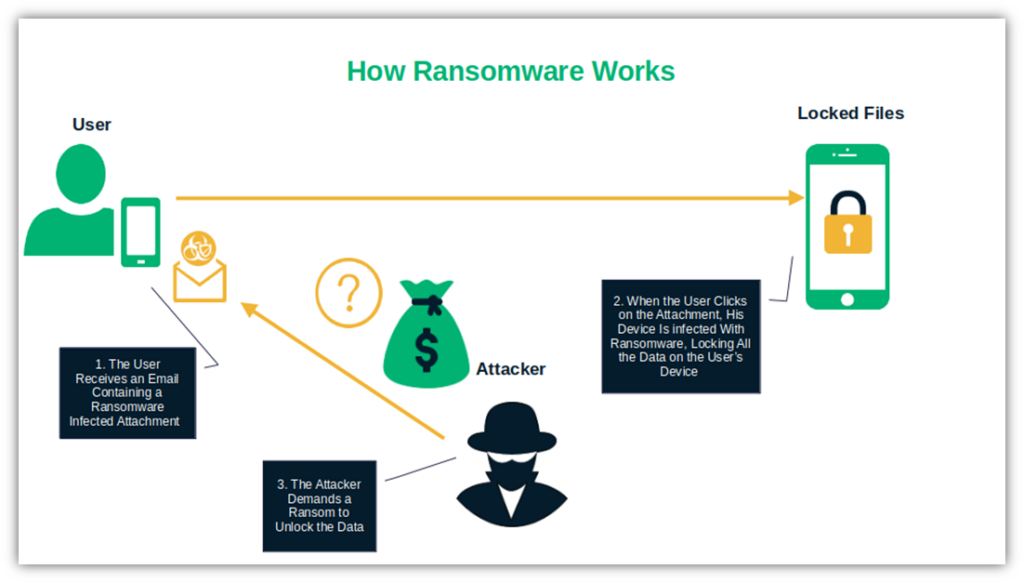
Nearly one in four companies interviewed by ExtraHoop consider ransomware the greatest risk to the security of their business. For small- and medium-sized businesses, the outlook looks even bleaker. According to Orange Cyberdefense, SMBs are impacted by ransomware four times more often than larger companies.
A Real-World Example of a Ransomware Attack
MediSecure, a small Australian online prescription provider, is a living witness to it. In May 2024, the company announced that it suffered a massive ransomware attack that lasted nearly four years, from March 2019 to November 2023.
Cybercriminals posted over 6.5 million terabytes of personal information and health data from 12.9 million Australians for sale on the dark web. That’s almost half the country’s population, which topped 26.9 million people as of December 2023.
As you can imagine, this didn’t end well. The company, which had only 17 employees, didn’t have enough funding to respond to the incident. As a result, it went into voluntary administration (i.e., an insolvency procedure) in June 2024. Game over.
But don’t scream like a banshee just yet as you read this… This example is just the beginning of the list of cyber security threats we have to share.
Cyber Security Threat #2: Malware Infections
Malware is a category of cyber security threats encompassing any malicious software created to harm devices or steal data. Ransomware, spyware, and viruses are all part of this creepy family that torments SMBs’ dreams.
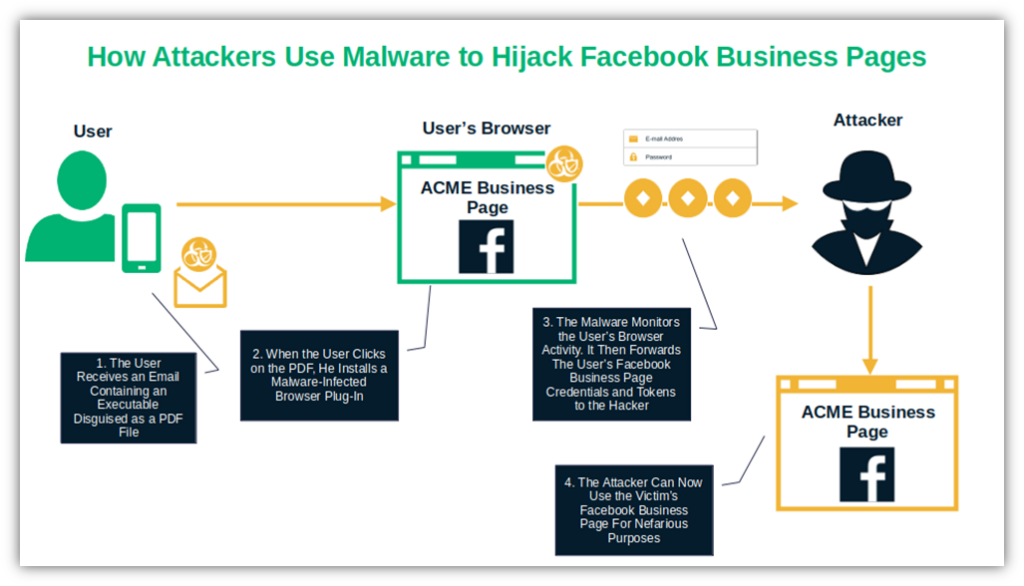
From March to May 2024, malware infections detected by SonicWall surged by 30%. In May alone, it increased by a whopping 92%. Yup, needless to say, malware infections are a frequent SMB cyber threat horror.
A Real-World Example of a Malware Attack
One of the last versions of Ducktail malware is a bone-chilling example of the dangers this cyber security threat poses to businesses and their customers. From March to October 2023, attackers sent out phony commercial emails in the name of major clothing companies. The messages included an attachment with pictures and a malware-infected executable with a bait name (e.g., commercial offers or price lists) disguised as an innocent PDF file.
When a recipient (e.g., an employee of one of the spoofed companies) clicked on it, the malware installed a malicious browser extension. Subsequently, the malware then monitored the targeted employee’s browser and hijacked their Facebook Business accounts by stealing their credentials and active session cookies.
Voila’. The bad actor was then able to use organizations’ Facebook Business pages to post inappropriate content, buy ads, or steal money from their customers. This chilling tale didn’t scare you enough? Keep on reading.
Cyber Security Threat #3: The Dreaded Phishing + Malware Combo
Phishing is a common technique bad guys use to trick users through deceptive emails, communications, or phony websites into revealing sensitive information (e.g., login credentials, credit card numbers, etc.). Its effects can be even more devastating when paired with malware.
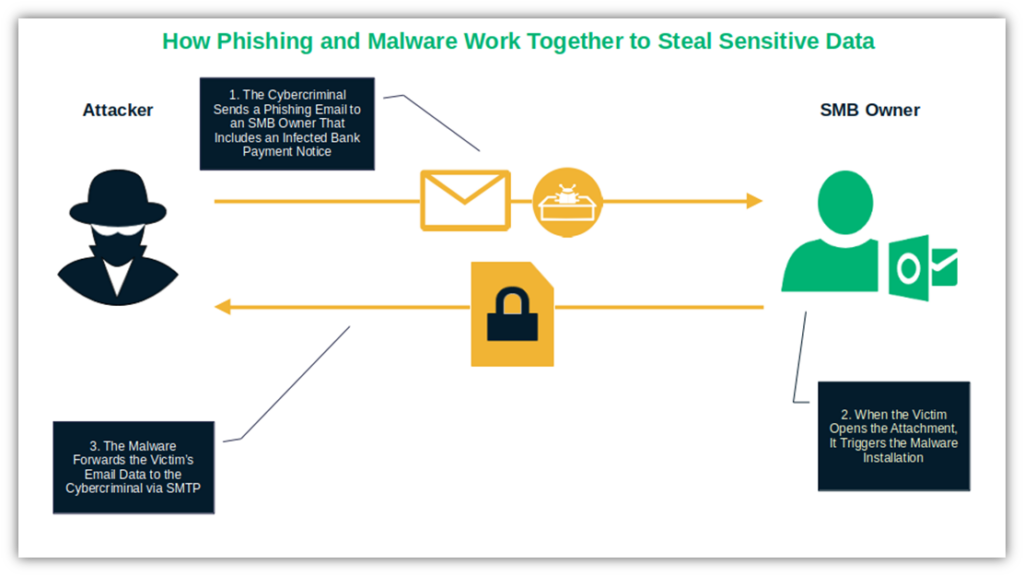
In 2023, SlashNext identified an average of 31,000 phishing-related cyber security threats per day. Six months later, the company announced more bad news: “SlashNext Mid-Year State of Phishing report shows 341% increase in business email compromise (BECs) and advanced phishing attacks”— a number like that is surely enough to give any SMB insomnia for months.
A Real-World Example of This Dangerous Combo Attack
In March 2024, Trustwave SpiderLabs identified another spooky threat that troubled the sleep of many SMBs. Targeted users received a phishing email masquerading as a bank payment notice. The messages included .zip or .rar archive files infected with the infamous keylogger malware Agent Tesla.
To keep the story short, the users opened the archive. In doing so, they triggered the info stealer’s installation through a malicious loader that was using obfuscation techniques (e.g., making the code difficult to read or understand) to avoid detection. This enabled threat actors to capture the victims’ email usernames and passwords.
Consequently, the malware leveraged compromised email accounts to steal data that would be transmitted over the simple mail transfer protocol (SMTP). Nowadays, it really seems that archive files are the new black for the bad guys.
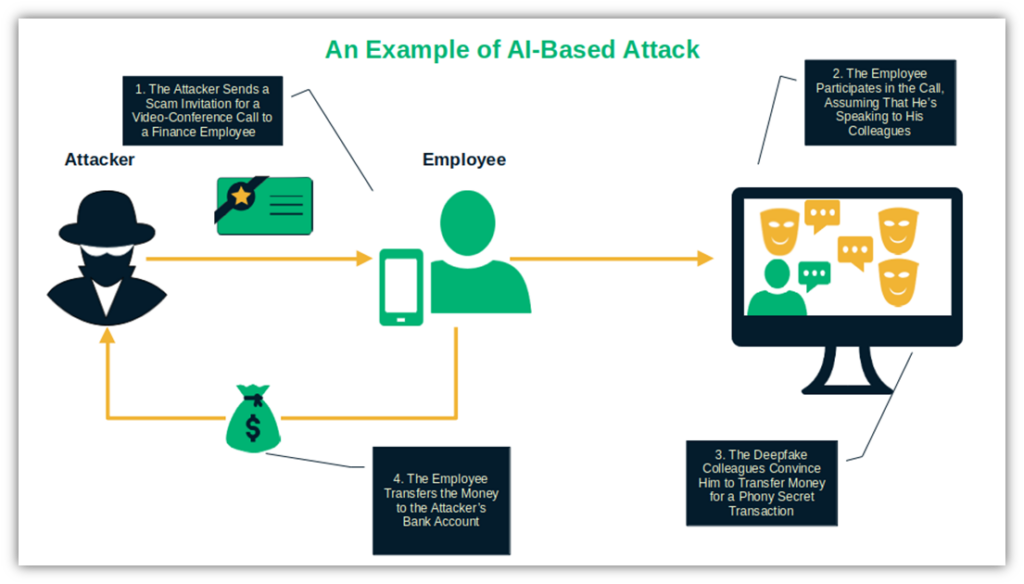
Cyber Security Threat #4: Artificial Intelligence (AI)-Based Attacks
AI attacks leverage artificial intelligence (AI) tools to generate credible phishing emails or to produce audio, images, and video that mimic real people to manipulate users’ behaviors. AI is also used to create classic or mutating malware (i.e., polymorphic malware) that can bypass conventional security measures.
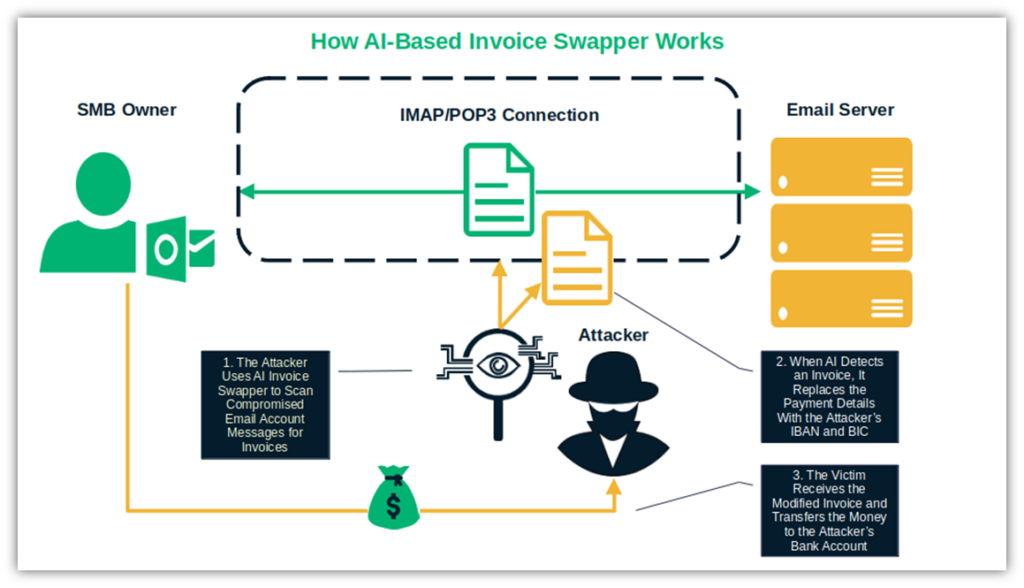
AI is the trendiest (and creepiest) boogeyman hiding under SMBs’ beds. According to Darktrace, 74% of organizations consider AI-based cyber security threats one of their top issues.
A Real-World Example of an AI-Based Attack
Gone are the times when cybercriminals had to go through a great deal of trouble to access your bank account to steal money. With AI, all the bad guys have to do is hack into your email, intercept invoices, and change your payment details to accounts they control.
This is exactly what happened to several businesses and individuals in Europe in 2024. Meet the “Invoice swapper.” This AI-based tool allows attackers to scan compromised email accounts using the internet message access protocol (IMAP) or the post office protocol (POP3) to detect messages containing invoices or payment information.
Once the program detects an invoice, it automatically swaps the legitimate payment details with the hacker’s fraudulent banking information. The recipient gets the invoice. Assuming that’s the real thing, they transfer the money to the attacker’s bank account.
AI is taking cyber threats to a whole new level of terror, but it isn’t the only trick up attackers’ sleeves…
Cyber Security Threat #5: Social Engineering Attacks
Social engineering encompasses the psychological manipulation techniques used by attackers to persuade a targeted individual to reveal sensitive information or perform specific actions (e.g., transfer funds to the hacker’s bank account). In these attacks, threat actors employ many tactics to manipulate their targets. More recently, the use of generative AI technologies (i.e., deepfakes) have played key roles in these situations.
Cisco’s 2024 Cybersecurity Readiness Index shows that only 2% of SMBs have the cyber readiness maturity to keep cyber security threats at bay. When you consider that social engineering attacks are one of the ghouls populating SMBs’ nightmares, this stat is pretty dismal.
Two Real-World Examples of Social Engineering Attacks
In the first example, a multinational organization, later revealed as the British engineering and design firm Arup, had a taste of one of these scams at the beginning of 2024. CNN reports that one of the company’s finance employees in Hong Kong received a fake email from a cybercriminal posing as the company’s chief financial officer (CFO) in the United Kingdom, inviting the target to a video conference about a confidential transaction.
As instructed, the employee attended the call with several other colleagues (or at least, he thought they were). Toward the end, they eventually agreed to transfer $25.6 million to a bank account. Unfortunately, those individuals the employee thought were real staff members turned out to be AI-generated “deepfakes.”
Luckily enough, fraudsters can’t fool everyone. In our second example, a Ferrari executive who was the target of a similar scam attempt recognized the deepfake for what it was before it was too late. Phew! A bit of gut feeling and a few subtle AI mechanical intonations that didn’t go unnoticed saved the day. Well done.
Cyber Security Threat #6: Unsecure Networks
Unsecured networks are a villain’s paradise and organizations’ versions of hell. An unsecured network is one that anyone can use (including crooks), as it typically has poor security protections (or none in place at all). They enable bad actors to intercept data and extract login information completely undisturbed.
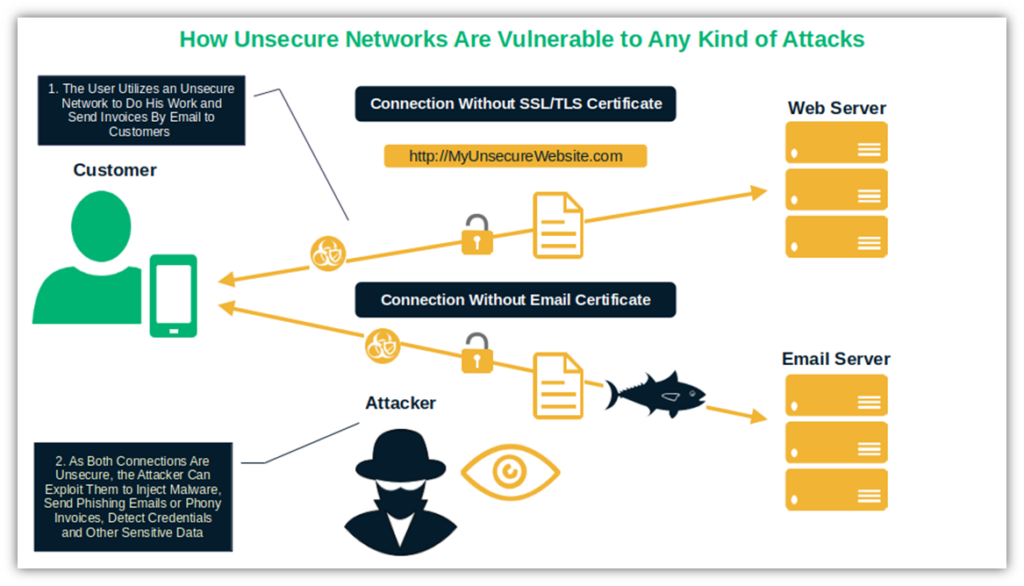
The specter of network cyber security threats never stops afflicting SMB owners. In Q2 2024, researchers at Cato CTRL noticed a 61% surge in attempts to maliciously exploit the Log4j vulnerability and a 79% increase in wide-area network (WAN) bound traffic compared to Q1 2024.
A Real-World Example of When Attackers Exploited an Unsecured Attack
The ghost of network cyber threats also visited Enrique Villaverde, a Spanish family business owner. Cisco shared how Megablok employees spent months dealing with unexplained network issues and customers complaining about receiving fake invoices from them. The company’s IT team was at a loss, and these issues seriously impacted the company’s productivity and reputation.
When they reached out to Cisco, the findings were shocking. Everything was wrong — from thousands of malicious connections and malware-infected endpoints to phishing emails and man-in-the-middle attacks sending phony invoices to customers.
Eventually, order was restored and the owner finally snapped out of his night terror, but at what price?
11 Moves That’ll Keep These Cyber Threats Nightmares at Bay
Start sleeping better at night by following these 11 quick tips.
- Protect your network, emails, and other data in transit. End-to-end encryption and digital certificates (i.e., secure socket layer (SSL)/ transport layer security (TLS) and email certificates) will do the trick.
- Keep software and systems up to date. Don’t procrastinate — install patches and software updates as soon as they’re available. This will help you patch holes in the software and systems that help keep your business running.
- Run regular malware and vulnerability scans on your website, devices, and other systems. Automate the process using tools like SiteLock to scan your website and identify vulnerabilities.
- Ensure you comply with the latest PCI DSS 4.0.1. If you accept online payments, abiding by the Payment Card Industry’s standards will help keep hackers at bay and avoid costly non-compliance fines from credit card companies. HackerGuardian is an intuitive solution that performs unlimited automated scans and provides you with a ready-to-submit PCI compliance report.
- Implement the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) Cybersecurity Framework (CSF) 2.0. The latest version of the framework includes dedicated sections to help SMBs in their never-ending battle against cybercriminals.
- Consider going passwordless wherever and whenever possible. Passwordless login solutions such as client certificates and other multi-factor authentication tools can be much more secure than traditional passwords when correctly implemented.
- Create and enforce a cyber security plan. Does this sound complicated? It doesn’t have to be. Check out our free SMB cyber security plan.
- Follow ransomware protection recommendations. CISA put together a list of free resources based on insights from the Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI), the National Security Agency (NSA), and the Multi-State Information Sharing and Analysis Center (MS-ISAC).
- Prioritize product security during the software procurement process. CISA has a comprehensive guide to help software developers get started.
- Educate your users. Teach them to identify phishing attacks, spam, malware, and other threats.
- Clean up your act by embracing cyber hygiene. Identify areas where your cyber defenses and practices are strong and where you’re lacking basic security hygiene.
Pro tip: Automate as much as you can. It’ll eliminate the manual burden on employees and give them back valuable time to focus on other priorities that require their critical thinking capabilities, knowledge, and skills.
Looking for other cyber security tips for small businesses?
We’ve got you covered with tips that will help make you a tougher target.
Final Thoughts About These 6 SMB Cyber Security Threats and How to Deal With Them
Every SMB owner has demons to fight. If even one of the six most common cyber security threats we’ve just listed “goes bump in the night” of your IT nightmares, start building up your protections against it.
Don’t let bad guys cost you another night’s sleep. Get your ZzZzs back on track by:
- Working on implementing a cyber security plan,
- Protecting your network and systems, and
- Investing in tools that’ll actively detect and stop threats 24/7, even when you’re sleeping.





















2018 Top 100 Ecommerce Retailers Benchmark Study
in Web Security5 Ridiculous (But Real) Reasons IoT Security is Critical
in IoTComodo CA is now Sectigo: FAQs
in SectigoStore8 Crucial Tips To Secure Your WordPress Website
in WordPress SecurityWhat is Always on SSL (AOSSL) and Why Do All Websites Need It?
in Encryption Web SecurityHow to Install SSL Certificates on WordPress: The Ultimate Migration Guide
in Encryption Web Security WordPress SecurityThe 7 Biggest Data Breaches of All Time
in Web SecurityHashing vs Encryption — The Big Players of the Cyber Security World
in EncryptionHow to Tell If a Website is Legit in 10 Easy Steps
in Web SecurityWhat Is OWASP? What Are the OWASP Top 10 Vulnerabilities?
in Web Security