What You Need to Know About PCI DSS 4.0 (and Version 4.0.1)
Is your organization ready to comply with the PCI DSS 4.0 requirements that will become effective in March 2025? Here’s what you need to know to integrate PCI DSS 4.0 (and revisions outlined in version 4.0.1) into your security framework and operations
The Payment Card Industry Data Security Standards (PCI DSS) is a set of security fundamentals that helps organizations handling payment card information avoid falling prey to cybersecurity incidents and data breaches. It also ensures they pay the consequences when they do. In 2022, the Payment Card Industry Security Standards Council (PCI SSC) published PCI DSS version 4.0’s first set of revised and new requirements.
Many of these standards requirements became effective on March 31, 2024 (with additional “best practices” that will be mandatory by March 31, 2025). However, in June 2024, they published PCI DSS version 4.0.1, which revises specific requirements to provide clarification and guidance but provides “no additional or deleted requirements” to PCI DSS version 4.0. So, don’t panic.
Now, it’s time to start preparing for the next PCI DSS 4.0 requirements that’ll kick into effect next year and ensure you’re also taking into account the clarifying revisions published in version 4.0.1.
PCI DSS 4.0 Phase Two: Dozens of New Requirements to Be Implemented Before Q2 2025
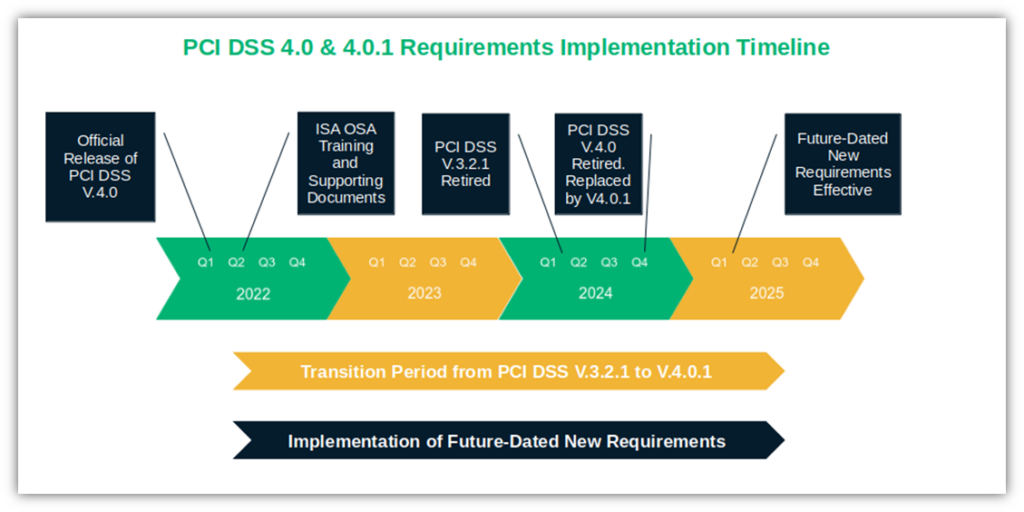
PCI DSS 4 introduced several fundamental changes to tackle emerging threats and security issues brought about by new technological advancements since the 2018 release of the previous version, PCI DSS 3.2.1.
PCI DSS version 4.0 includes in total 64 new requirements. With the first phase of 13 new requirements done and dusted, the next stage includes rolling out the remaining 51 new PCI DSS 4.0 requirements. Currently considered “best practices,” they’ll come into force no later than March 31, 2025. (NOTE: Not all requirements may apply to you, as some are specific to service providers.)
We get it, that’s a lot to digest. To help you, we’ve prepared an overview of these second-phase requirements and a few tips. It’ll enable you to better understand the new rules and how best to address them.
Check the summary table and/or go into the nitty-gritty sections below. (NOTE: We skipped listing the new requirements under Principal Requirements #1 and #2 since they went into effect when PCI DSS 4.0 rolled out).
| Changed PCI DSS Version 4.0 Requirements That Are “Best Practices” Until March 31, 2025 | PCI DSS 4 — Summary of Changes (New or Amended Requirements) | Tips to Help You Comply with Some of These New Requirements |
| Requirement 3: Protect Stored Account Data | These changes are related to the protection of sensitive authentication data (SAD) and primary account numbers (PANs) through encryption and cryptographic hashes. | Use strong cryptographic hash functions and algorithms.Limit the usage of disk-level encryption.Ensure secure cryptographic key storage |
| Requirement 4: Protect Cardholder Data with Strong Cryptography During Transmission Over Open, Public Networks | These new and amended requirements focus on cryptography-related roles and responsibilities, and certificate and key validity and inventory. | Use certificate management software such as Sectigo Certificate Manager or DigiCert CertCentral to verify the validity of your SSL/TLS certificates.The same tools will help you keep an inventory of keys and certificates. |
| Requirement 5: Protect All Systems and Networks from Malicious Software | These new clauses emphasize the implementation of regular malware scanning and phishing protection. | Review your components and implement supply chain security best practices.Run daily malware scans using only trusted and well-known anti-virus/malware tools such as SiteLock.Train your users to recognize and avoid phishing scams and malware threats. |
| Requirement 6: Develop and Maintain Secure Systems and Software | New requirements focusing on software security and system threat prevention through automation and secure practices. | Create an SBOM to list all application’s open source components, their licenses, versions, and patch status. Sign it with a trusted code signing certificate.Invest in Website security checker tools like SiteLock. HackerGuardian will even monitor your PCI DSS version 4 compliance.Shield your payment page scripts from cross-site script (XSS) attacks following OWASP’s suggestions. |
| Requirement 7: Restrict Access to System Components and Cardholder Data by Business Need to Know | These new requirements address regulated access to systems and cardholder data. | Implement access control policies as described in the OWASP Authorization cheat sheet.Follow the principle of the least privilege (POLP).Delete unused accounts. |
| Requirement 8: Identify Users and Authenticate Access to System Components | These changes mandate additional measures to secure access and passwords. | Implement multifactor authentication (MFA) wherever possible.Shield credentials from malicious snoopers and man-in-the-middle attacks (MITM) with an SSL/TLS certificate.Never hardcode passwords. |
| Requirement 9: Restrict Physical Access to Cardholder Data | This single point highlights the importance of securing all physical points of interaction (POI and access to cardholder data). | Inspect them regularly.Stay up to date with new threats. Check the NIST National Vulnerability Database (NVD) and MITRE’s common vulnerabilities exposure (CVE) database. |
| Requirement 10: Log and Monitor All Access to System Components and Cardholder Data | These requirements encompass the actions that are required for effective log management and analysis. | Don’t miss OWASP log implementation best practices. Automate log analysis and monitoring with the support of paid or open-source log analysis tools.Encrypt your log using strong encryption algorithms, apply strict access control policies, and review them often. |
| Requirement 11: Test Security of Systems and Networks Regularly | The newly added clauses emphasize the need for testing systems and networks to fix all vulnerabilities found and protect payment pages from unauthorized modifications. | Scan systems with SiteLock Pro and Business.Schedule and run over 30,000 vulnerabilities and XSS attack tests with HackerGuardian.Implement an alert system for HTTP headers of payment pages and content’s unauthorized modifications. |
| Requirement 12: Support Information Security with Organizational Policies and Programs | All changes related to this requirement are centered on security policies and programs, including those involving third-party service providers (TPSPs). | Inform your peers and employees.Set up ad hoc training sessions.Review and keep all information up to date. |
PCI DSS 4.0 — Requirement 3: Protect Stored Account Data
According to BlackFog’s latest report, 92% of ransomware attacks analyzed in the first four months of 2024 were used to extract data. This PCI DSS version 4 section includes new requirements related to the protection of sensitive data at rest (i.e., saved in a digital form). They all align perfectly with BlackFog’s findings.
Specifically, these changes mandate enterprises to protect sensitive authentication data (SAD) and primary account numbers (PANs) through encryption and cryptographic hashes.
To achieve compliance, you may want to:
- Use strong mathematical encryption algorithms. Follow industry standards. For instance, use the secure algorithm SHA-256 to make PANs and SAD unreadable, and use robust asymmetric algorithms, too. Moreover, get ready for quantum computing by adopting hybrid post quantum cryptography (PQC) algorithms.
- Opt for keyed cryptographic hashes. In other words, use the hash message authentication code (HMAC) with two cryptographic keys (computed from one key) to preserve data authenticity and integrity.
- Limit the usage of disk-level encryption. Encrypt PAN data only at the disk or partition levels. This way, the data will be indecipherable when stored on removable hardware.
PCI DSS 4.0 — Requirement 4: Protect Cardholder Data with Strong Cryptography During Transmission Over Open, Public Networks
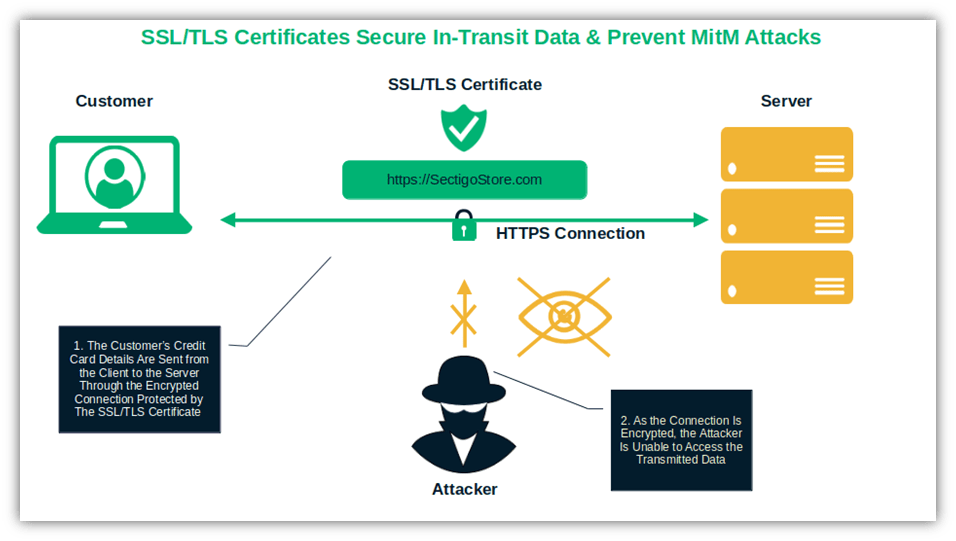
Is your website part of 96% of internet Google traffic protected by a secure socket layer/transport layer security (SSL/TLS) certificate? We bet it is. Unfortunately, that isn’t enough to prevent the bad guys from snooping/stealing sensitive data transmitted over the network.
Protect your organization and customers from man-in-the-middle attacks (MITM).
- Check that your SSL/TLS certificates are still valid. Certificates don’t last forever. Use certificate management software such as Sectigo Certificate Manager to keep expired or revoked certificates under control. It’ll be particularly helpful now that Google has announced that it might require SSL certificates with a mandatory 90-day validity period.
- Keep an inventory of keys and certificates. The same tools we’ve just mentioned will give you a complete and up-to-date picture of all your secrets and keys.
PCI DSS 4.0 — Requirement 5: Protect All Systems and Networks from Malicious Software
In 2023, the total malware volume identified by SonicWall increased globally by 11%. Zscaler discovered 745 million more attacks than in 2022. The new clauses included in this group focus on malware prevention through periodical components evaluation, regular malware scanning, and phishing protection.
- Harden the security of your supply chain. ReversingLabs detected a 1,300% increase in malicious components in just three years (2020-23). Periodically review your components’ security and implement supply chain security best practices.
- Scan your software for malware. Run daily malware scans using only trusted antivirus/antimalware tools such as SiteLock. Use more than one for comprehensive detection. Don’t rely on free scanners as they may be out of date.
- Train your users. EvilProxy (a phishing attack that managed to bypass multifactor authentication [MFA]) and QR code phishing are just two examples of the potential consequences of untrained users. Turn click-enthusiast users into cybersecurity guards. Teach them about phishing and show them how to recognize phishing emails and attacks.
PCI DSS 4.0 — Requirement 6: Develop and Maintain Secure Systems and Software
2.8 million personal data of Sav-Rx clients, a pharmacy benefit management company, were stolen in October 2023. A lack of advanced threat detection and monitoring procedures was among the identified vulnerabilities. This confirms the need to focus on threat prevention through automation. Precisely what this section’s updates are about. Here are our suggestions to help you reach compliance:
- Create and request software bills of materials (SBOMs). SBOMS are gaining popularity, being supported by 75% of cybersecurity leaders in 2023. These detailed breakdowns of software components were included in the U.S. White House‘s Executive Order (EO) 14028. Each SBOM lists all an application’s open source components, licenses, versions, and patch status. It’s an editable file; therefore, once generated, don’t forget to protect its integrity with a trusted code signing certificate.
- Invest in an automated website security checker tool. Manually detecting and blocking web-based attacks in real time is virtually impossible to do manually, as there’s too much noise and data to get through. Website security checker tools like SiteLock will do the job in a breeze. HackerGuardian will even monitor your PCI DSS version 4 compliance, suggest fixes, and generate a ready-to-submit PCI DSS compliance report.
- Protect your scripts. Implement OWASP’s recommendations to shield your payment page from cross-site script (XSS) attacks. Ensure 24/7 automated XSS and other attack detection with Sectigo SiteLock Website Security scanner. From restricting unsafe scripts to content security policies, OWASP’s Content Security Policy cheat sheet is a goldmine of tips and tricks.
PCI DSS 4.0 — Requirement 7: Restrict Access to System Components and Cardholder Data by Business Need to Know
In February 2024, about 1,300 American Express cardholders’ data were exposed due to unauthorized access to a third-party service provider’s system. Boost the security of your components and cardholder data to comply with these changes before the bell rings in March 2025.
- Implement access control policies. Broken access control is the top threat listed in the OWASP Top 10 Web Application Security Risks. Don’t be too generic. Your policies should cover all user roles, systems, and data they can access to. Short of ideas? Check out the OWASP Authorization Cheat Sheet.
- Follow the principle of the least privilege (POLP). “You shall not pass,” declared Gandalf in The Lord of the Rings. Tell unauthorized third parties the same. Disable access to data by default. Grant access to only whom and what is required. For instance, an administrator doesn’t need to view cardholders’ data to grant viewing access to them, right?
- Delete what’s not needed. Did a user change roles or departments? Did you stop dealing with a third party who had access to your systems? Don’t wait — delete their accounts immediately to remove unnecessary access.
PCI DSS 4.0 — Requirement 8: Identify Users and Authenticate Access to System Components
Over 75% of U.S. users surveyed by Forbes Advisor in 2024 admitted having their personally identifiable information (PII) stolen through hacked accounts. Yup. This section is all about securing accesses and passwords with different methods.
- Implement multifactor authentication (MFA) wherever possible. Require users looking to access your cardholder data environment (CDE), and other systems to provide two or more verification factors (e.g., a password and a one-time security code or a secure token).
- Shield credentials from malicious snoopers. Protect applications and system passwords in transit from man-in-the-middle attacks (MITM) with an SSL/TLS certificate. The encrypted connection will scramble the transmitted data. Try to steal and/or use those encrypted data now, hackers!
- Never hardcode passwords. According to GitGuardian’s 2023 scan data, 8 million GitHub commits exposed at least one secret (e.g., credentials or keys). The takeaway? Don’t hardcode credentials. Use secret scanners (GitHub offers a free one too) to detect and delete them.
PCI DSS 4.0 — Requirement 9: Restrict Physical Access to Cardholder Data
Did you know that point of sale (POS) terminals and points of interaction (POI) are subject to vulnerabilities as well and can be disabled via ransomware attacks, too? No one and nothing is safe in the digital world. To protect your POI:
- Set up regular inspections. Check your POI’s hardware and software. A checklist based on potential risks and new known vulnerabilities will ensure no stone will be left unturned.
- Stay up to date with new threats. Subscribe to vulnerability catalog updates and cybersecurity newsletters. The NIST National Vulnerability Database (NVD) and MITRE’s common vulnerabilities exposure (CVE) database are two of the best sources you can refer to.
PCI DSS 4.0 — Requirement 10: Log and Monitor All Access to System Components and Cardholder Data
We get it: effective log management and analysis is never easy. It gets even more complicated if your organization logs an average of 9.5 billion events a day, as Klaviyo does. However, logs are a vital component for security incident detection/response and PCI DSS 4.0 compliance.
Once again, OWASP comes to the rescue with some log implementation best practices. On top of it:
- Automate log analysis and monitoring. There are a plethora of paid and open-source log analysis tools out there. Pick one or more. They’ll help you detect and promptly address suspicious access to system components and cardholder data. Spotting critical security control issues won’t be a problem either.
- Safeguard your logs. Access logs to system components and cardholder data contain sensitive information. Use strong encryption algorithms. Apply strict access control policies against unauthorized access, and tampering.
- Review your logs often. Check your logs for anomalies or suspicious activities (e.g., too many failed logins in a short period of time, accesses from dodgy IP addresses or countries, etc.).
PCI DSS 4.0 — Requirement 11: Test Security of Systems and Networks Regularly
In Q1 2024, Kaspersky reports that MITRE’s CVE Program registered 3,965 vulnerabilities. That’s an average of 1,321 vulnerabilities per month in those first three months!
Periodically testing systems and network security is the core of this section. It’ll guarantee that vulnerabilities and security issues are identified and addressed promptly and minimize the risk of leaks and fraudulent activities.
- Scan systems with Sitelock Pro or Business. Both tools will help you find system flaws before the bad guys do. They’ll automatically check and patch your core applications, websites, content management systems (CMSs), and more. And you’ll get a warning email every time an issue is found.
- Run thousands of diagnostic tests. Schedule your vulnerability tests with HackerGuardian PCI Compliance tool. It can scan up to 20 servers (depending on the package chosen). You’ll get a super detailed report based on over 30,000 diagnostic tests.
- Set up alerts for critical unauthorized changes. Implement an alert system for payment pages’ unauthorized modifications to HTTP headers and content. Use the tools suggested above to scan your website for potential XSS. Don’t miss the OWASP secure headers project page and the related cheat sheet for additional tips.
PCI DSS 4.0 — Requirement 12: Support Information Security with Organizational Policies and Programs
This last section highlights the importance of organizational policies and programs for effective card data protection. However, when employees are blissfully unaware of such procedures and standards, all sorts of security issues are right around the corner. Verizon’s latest report proved it: 68% of data breaches in 2023 involved human error (i.e., non-malicious human actions).
- Inform your peers and employees. Publish all security procedures, guidelines, and policies on your internal website to facilitate access to employees and stakeholders.
- Set up ad hoc training sessions. Train your personnel with courses online or in-person sessions. Include a short final verification test to validate their acquired knowledge.
- Review and keep all information and software up to date. Technology changes fast and so do attackers’ strategies and approaches. Harness the power of checklists to review the security of all your hardware, software, and protocols. Last but not least, always choose the latest cryptographic cipher suites. They are the most secure.
This is it. A neat overview of PCI DSS 4.0’s changes coming into effect by Q2 2025. Don’t stop reading. There’s more to know before kicking off your compliance activities.
PCI DSS 4.0: Which Requirements Apply to My Organization?
All companies handling payment data or accepting credit, debit, or digital card payments must be PCI DSS 4.0 compliant. However, not all businesses are created equal. For instance, service providers have 10 supplementary requirements to satisfy by March 31, 2025 before reaching compliance. (There are 11 service provider-related new requirements total in PCI DSS version 4.0, but one was effective immediately.)
This means that mom-and-pop shops won’t have to meet the same standards required of big corporations and enterprises.
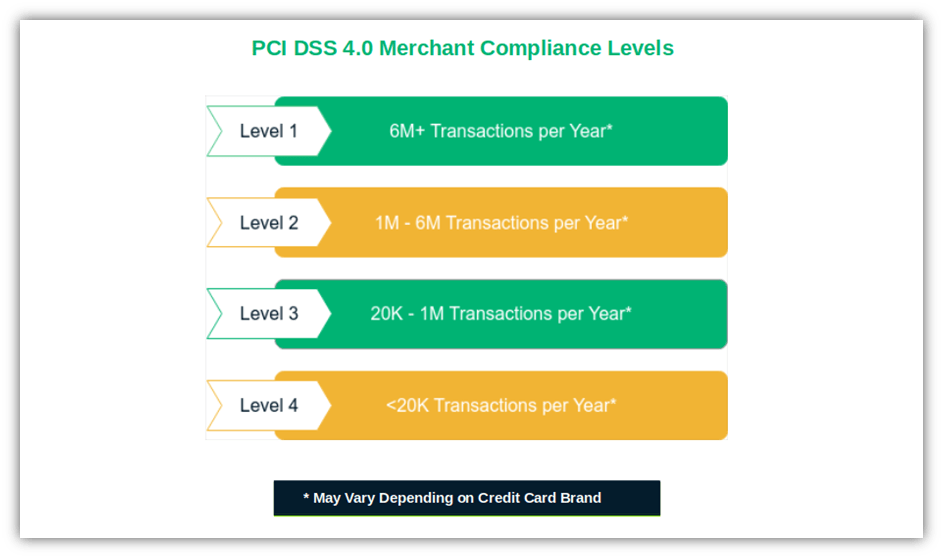
To this effect, the PCI Security Standards Council created four different compliance levels based on credit card transaction volume. Each level requires the implementation of a specific set of security control rules.
Before plunging into the PCI DSS 4.0 list, check out our merchant compliance comprehensive guide and do a first PCI self-assessment. You’ll immediately find out which level your organization fits into and its requirements.
Why SSL Certificates and Code Signing Are Important for PCI Compliance?
Every time a customer makes a payment online, their credit/debit card or banking information is at risk of falling into the wrong hands. Phishing is another dangerous threat plaguing businesses accepting payments online. In 2023, Zscaler identified 745 million more attacks than in 2022, marking a 58% increase year over year.
And before you say it, nope, this likely isn’t only due to some scanning tool improvements. Other software security providers noticed the same trend. Bolster, for example, recorded a 94% growth in phishing attacks since 2020.
So, an SSL/TLS certificate issued by a trusted certificate authority (CA) will:
- Protect your websites from MITM attacks. The certificate uses a 256-bit encryption key to scramble the information in transit between the client and the server, making it virtually impossible for an attacker to decrypt it.
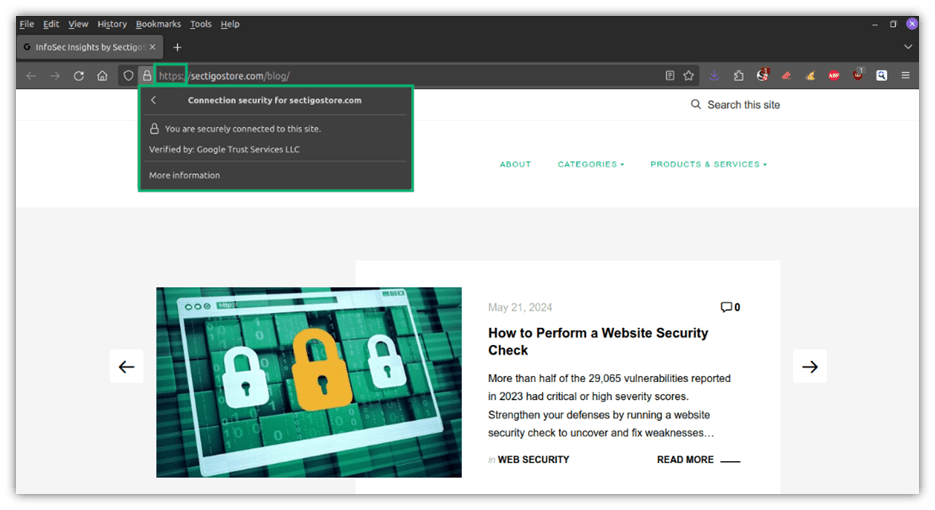
- Shield you from phishing attempts. On websites protected by SSL/TLS certificates, users can confirm the legitimacy of the site by verifying the website’s owner identity (so long as the site owner opted for an organization- or extended-validation certificate). The URL will also start with “HTTPS” (hypertext transfer protocol secure) to further reassure the user about the security of the page, showing the connection is encrypted.
- Help you achieve PCD DSS 4 and 4.0.1 compliance. SSL/TLS certificates are the backbone of PCI DSS compliance. They offer strong private keys and the latest cipher suites. Likewise, it guarantees that cardholders’ data are stored and transmitted securely. Without it, compliance isn’t possible.
Last but not least, trusted code signing certificates will also, even if indirectly, help you reach PCI DSS 4.0 compliance. Add another layer of security against attacks by installing only signed plug-ins and components, and by signing SBOMs for software you create. And if you develop your own software or plug-ins, even just for internal use, code signing with a publicly trusted digital certificate is something you can’t do without. It can help you meet PCI SSC’s Software Standards’ security requirements.
Final Thoughts About What You Need to Know About PCI DSS 4.0
Preparing for PCI DSS version 4.0’s March 2025 deadline will take organizations time and work. However, understanding the changes is the first step to reaching compliance. The good news is that the things we’ve listed here today are things that every security-conscious organization should already be doing.
Put to good use what you’ve just learned. Start addressing the latest PCI DSS 4 requirements today by following the tips included in this article.
- Use SSL/TLS certificates to secure your sites and web apps to keep connections private and protect cardholder data during transmission over the network.
- Create, maintain, and digitally sign an SBOM as an inventory of your software.
- Invest in a malware and PCI-DSS compliance scan tool like HackerGuardian.
It’ll protect your organization and customers’ sensitive data, make your reputation shine, increase customers’ trust, and, in case of a data breach, it’ll help you minimize losses and avoid fines.




















2018 Top 100 Ecommerce Retailers Benchmark Study
in Web Security5 Ridiculous (But Real) Reasons IoT Security is Critical
in IoTComodo CA is now Sectigo: FAQs
in SectigoStore8 Crucial Tips To Secure Your WordPress Website
in WordPress SecurityWhat is Always on SSL (AOSSL) and Why Do All Websites Need It?
in Encryption Web SecurityHow to Install SSL Certificates on WordPress: The Ultimate Migration Guide
in Encryption Web Security WordPress SecurityThe 7 Biggest Data Breaches of All Time
in Web SecurityHashing vs Encryption — The Big Players of the Cyber Security World
in EncryptionHow to Tell If a Website is Legit in 10 Easy Steps
in Web SecurityWhat Is OWASP? What Are the OWASP Top 10 Vulnerabilities?
in Web Security