What Is A Server Certificate?
A server certificate is an SSL certificate issued to hostnames that includes machine names (like XYZ-SERVER-04) or domain names (like www.example.com). When a client sends the request, the browser will verify the server certificate to ensure the legitimacy of the web host.
An SSL server certificate is a digital certificate issued to the server for two main purposes – to authenticate the server’s identity and create a secure communication channel with the client. The SSL server certificate uses public key infrastructure (PKI) to maintain the integrity and confidentiality of the data.
A server security certificate or a web server certificate is what is more commonly known to us as an SSL/TLS certificate. An SSL server certificate serves two primary purposes:
- It affirms the identity of the server before authenticating it.
- It establishes an encrypted channel for communication between the server (the website) and the client (the end user’s browser that connects to it).
Sectigo Server SSL Certificates from $8.78/year!
Get the lowest prices on trusted SSL certificates from Sectigo.
Shop for Sectigo SSL CertificatesAn SSL certificate is a digital file that consists of a public and private key pair. The private key is stored on the server, whereas the public key is bundled together with the certificate and is shared with the client during the SSL handshake. Once the certificate is installed on the webserver, it switches the protocol to HTTPS, and the secure padlock symbol appears on the site. Web server certificates help to maintain data confidentiality and data integrity.
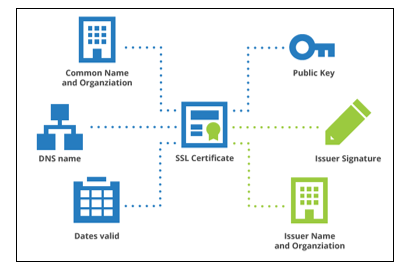
All SSL server certificates purchased from third-party trusted certificate authorities (CAs) use standard encryption protocols. With an SSL server certificate installed on your web server, you won’t need to worry about an attacker listening in on the network and stealing sensitive information.
SSL Webserver Certificate
A web server certificate is basically an SSL certificate issued to a web server to authenticate its identity to the client. The web server certificate also establishes a secure communication channel with the client for more robust protection.
An SSL web server certificate is an X.509 digital certificate that is meant to perform two fundamental functions:
- To authenticate the identity of the webserver
- To establish a secure communication channel between the client and server
The SSL web server certificate is digitally signed by a certificate authority (CA) and follows the CA/Browser forum standards.
The Benefits of an SSL Server Certificate
Now that we know what an SSL server certificate is, let us look at some of its benefits:
- Data Privacy and Data Integrity. Data is encrypted as it travels over the wire so that it cannot be stolen or tampered. Even if attackers try a man in the middle attack, they will be left with garbled information in an unreadable form that cannot be decrypted without the private key.
- Assurance of Server Identity. SSL certificates affirm the identity of the server before authenticating it and assures that it is who it claims to be. Identity verification is a critical aspect of web security.
- Builds Customer Trust. The presence of a padlock on the address bar instills trust in customers. Besides, Google’s endeavor to flag all websites still running on HTTP necessitates installing an SSL/TLS certificate.
A Breakdown of Each Type of SSL Server Certificate:
SSL/TLS certificates are categorized based on their functionality and validation levels. There are three validation levels, namely, domain validation (DV), organization validation (OV), and extended validation (EV).
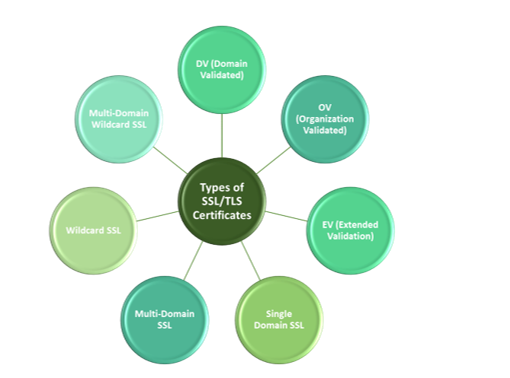
Let’s take a quick look into these categories to determine the differences between server security certificate types:
Domain Validation (DV) SSL Certificates — These types of certificates require the least stringent of all forms of validation. With DV, the CA simply verifies whether the applicant’s domain ownership rights. A DV certificate is inexpensive and can be issued in minutes.
Organization Validation (OV) SSL Certificates — OV certificates are designed for enterprise environments. When it comes to organization validation, the CA not only assesses the applicant’s rights to the domain name but also conducts additional investigations to determine the legitimacy of the organization at a basic level. OV certificates take a day or two to be issued.
Extended Validation (EV) SSL Certificates — EV certificates, as the name suggests, entails a much more rigorous vetting process. The CA performs an intense verification where the applicant is required to submit acceptable documentation to prove that they have a genuine business. Typically, it takes longer to issue an EV certificate since the company needs to be vetted thoroughly.
Single Domain SSL Certificates — A single domain SSL server certificate secures only one fully qualified domain name in one certificate.
Multi-Domain SSL Certificates — Multi domain web server certificates, also called UCC/SAN (unified communications certificates and subject alternative name) certificates, cover multiple domains in one certificate. For example, www.yourdomain.com, www.site.com, www.mydomain.net, etc. can be secured under one certificate.
Wildcard SSL Certificates — A wildcard SSL web server certificate utilizes one certificate to secure an unlimited number of first-level subdomains. For example, *.domain.com will cover blog.domain.com, products.domain.com, etc. If you wish to secure second-level subdomains, you’ll need to either purchase a second wildcard or get the next type of certificate.
Multi-Domain Wildcards — The most versatile of all, a multi-domain wildcard SSL certificate is a combination of wildcard SSL and SAN certificate. In a single certificate, it can secure up to 250 domains and multiple levels of accompanying subdomains.
Secure a Website in Few Clicks – Save Up to 79%
Save 79% on Sectigo SSL Certificates. It includes unlimited server licenses, reissuances, 256-bit encryption, and more.
SSL Server Certificate: How Do You Get One?
An SSL server certificate is a digital certificate issued to the server for two main purposes – to authenticate the server’s identity and create a secure communication channel with the client. The SSL server certificate uses public key infrastructure (PKI) to maintain the integrity and confidentiality of the data.
Now that we have discussed the benefits, validation levels and functions of SSL certificates, the question now is what needs to be done to get installed on your servers? Let’s break it down into five simple steps!
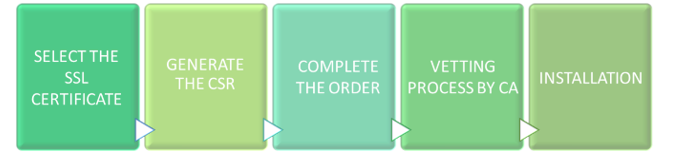
- Choose an SSL Certificate. Considering the different types of web server certificates available in the market today, it can be a daunting task to find one that fits your business requirements. Weigh your options based on your desired certificate validation level and functionality.
- Generate a certificate signing request. Once you have decided on the certificate, you’ll need to generate a certificate signing request (CSR). Fill in your information correctly as the CA will verify these details.
- Complete the Order Process. After completing the CSR, complete the order process and wait for the order confirmation mail from the CA. It will contain a link to submit your CSR.
- Await the CA to Complete Its Investigation. Once the order gets submitted from your end, the CA will conduct an investigation whose intensity will depend upon your certificate’s validation level.
- Download and Install Your Certificate. Following the vetting process, the CA will share your certificate files via email. These must be downloaded, and the certificate can then be installed based on your server.

 (32 votes, average: 4.50 out of 5)
(32 votes, average: 4.50 out of 5)