What is a CA signed certificate, why is it trusted, and how do you choose the best one for your site?
All the digital certificates that are signed by a publicly trusted certificate authority (CA) are considered to be CA signed certificates. Although the term “CA singed certificate” is frequently used to describe an SSL/TLS certificate, it also includes other types of X.509 digital certificates such as code signing certificates, email signing certificates, and document signing certificates. A CA signed certificate is trusted by all the browsers, email clients, and operating systems.
In this article, we’ll answer why the CA signed certificates are considered safe and how to choose the most suitable certificate as per your needs and budget.
Why CA Signed Certificates Are More Trusted Than a Self-Signed Certificate?
All the digital certificates have two basic security pillars: 1) encryption and 2) identity assurance. The guidelines for both of these aspects are regulated by The Certificate Authority/Browser Forum (CA/B Forum). All the publicly trusted CAs must follow those tight regulations in order to get trusted by the browsers. These guidelines include:
- Procedures to be followed for verifying the identity of the applicant;
- Technological features;
- Adherence to expiry dates and renewals procedures;
- Consequences for mis-issuance of a certificate; and
- Certificate revocation criteria and procedures.
The alternative to the CA signed certificate is the self-signed certificate, which is signed by the organizations or website owners themselves. The encryption generally remains the same, but another important security pillar, “identity assurance,” is missing here. Plus, self-signed certificates aren’t directly regulated by the CA/B Forum and, as a result, suffer many shortcomings.
Why Self-Signed Certificates Aren’t Trusted
For example, you can’t trust the validity date of a self-signed certificate. Unlike CA signed certificates which expires in two years after date of issuance, self-signed certificates’ validity period can differ, depending on what system you use to issue it. Here, the user can always generate and sign a new certificate containing a valid date range, and hence chances of its misusage increases.
Another example is something known as revocation ambiguity. With a CA signed certificate, the CA has the authority to revoke the certificate immediately if it’s misused. But with a self-signed certificate, there’s no real mechanism to revoke it. You can stop trusting it by removing it from the list of trusted certificates, but that’s about it.
Because such mismanagement is not possible with a CA signed certificate, they’re trusted to issue and sign all the digital certificates. All the browsers trust these certificates and show standard trust indicators.
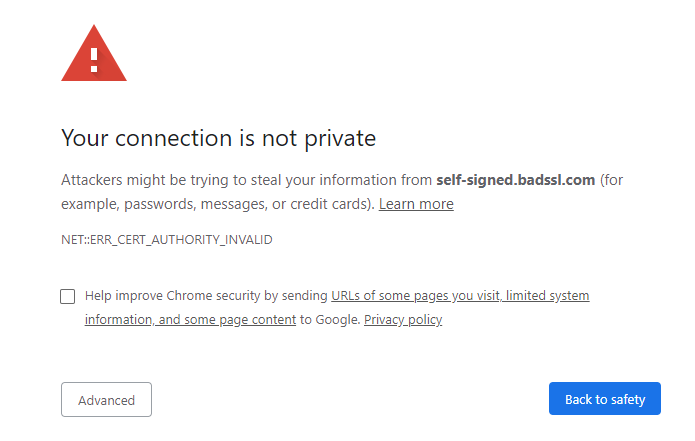
While browsers show security warning page with the error ERROR_SELF_SIGNED_CERT”, “SEC_ERROR_UNTRUSTED_ISSUER” OR “ERR_CERT_AUTHORITY_INVALID” for self-signed certificates. The users have to click on the Accept Risk button to access the website.
Are CA Signed Certificates Secure?
Yes, as we mentioned earlier, all CA signed certificates must follow the latest technological guidelines stipulated by the CA/B Forum. For example, according to the latest standards, no CA can issue an SSL certificate with a SHA-1 algorithm. Most of the CA signed certificates support up to 256-bit encryption and a 2048-bit RSA signature key. Although the actual key strength is dependent upon your server and browser configurations, all of the most popular CAs proactively offer the latest and highest technological features with their certificates.
Plus, the majority (but not all) of CA signed certificates offer third-party warranties, too! They’re bound to pay the victims up to warranty amount in case of encryption failure or mis-issuance of the certificate.
The Most Popular Certificate Authorities for CA Signed Certificate
Some of the most popular certificate authorities include Sectigo (formerly Comodo CA), DigiCert, Thawte, Symantec, GeoTrust, RapidSSL, GoDaddy, GlobalSign, and Entrust.
Among them, Sectigo’s PositiveSSL and InstantSSL certificates offer the most affordable CA signed SSL certificate options on the market. For example, a basic PositiveSSL certificate starts as low as $8.78 per year, with a generous $50,000 warranty and a dynamic site seal.
Types of CA Signed Certificates
All the digital certificates issued and signed by the publicly trusted certificate authorities come under the umbrella term “CA signed certificate.”
These are the four famous CA signed certificates:
- SSL/TLS certificates
- Code signing certificates
- Email signing certificates
- Document signing certificates
SSL/TLS Certificate
These certs are used by website owners to protect the data in transit between a website and a browser. A CA signed SSL certificate enables data encryption using the principles of public key infrastructure (PKI) and vets the identity and domain ownership of the applicant to make sure the data is directed to and decrypted by the intended endpoint only. It protects the websites from man-in-the-middle (MitM) attacks.
SSL certificates are classified in two ways:
- Utility/functionality wise: single domain, wildcard, multi-domain, and multi-domain wildcard SSL certificates
- Verification wise: domain validated (DV), organization validated (OV) and extended validated (EV)
Code Signing Certificates
Software developers and publishers use a code signing certificate to protect downloadable software such as device drivers, applications, executables, and scripts. It gives assurance about the software’s integrity and identity of the publisher.
There are two types of code signing certificates:
- Organization validated/individually validated
- Extended validated
Email Signing Certificate
A secure email certificate, also known as an S/MIME certificate or an email signing certificate, is used to secure sensitive business data that’s transferred via email. It attaches the sender’s digital signature to the email and encrypts the email contents (end-to-end encryption) to protect them both while they’re in transit and at rest. This type of certificate can help protect users from email spoofing attacks.
A CA signed email signing certificate starts from at as little as $12.95 per yearDocument Signing Certificate
Businesses and other organizations use this type of certificate to secure the sensitive business documents that they send over email and other electronic mediums via the internet. Just like email signing certificate, a document signing certificate enables the user to insert their digital signature on the document using their unique private key. The content of the document and the digital signature gets hashed, so that no tampering can go unnoticed. The intact hash value is the proof of the document’s integrity and authenticity.
It’s one of the best tools to prevent data theft and unauthorized data tampering.
A CA signed document signing certificate starts from at as little as $12.95 per year

 (31 votes, average: 4.87 out of 5)
(31 votes, average: 4.87 out of 5)