If a recent visit to some website has caused you to wonder what causes the “NET ERR_CERT_COMMON_NAME_INVALID” error on Google Chrome, you’ve come to the right place to get all your answers!
Certificate errors, along with their security warnings, can leave us confounded and worried. This is particularly true in the current digital landscape where cyber-attacks are on the rise. The word on the street is that cybercriminals are already using HTTPS to mislead users into believing their phishing websites are legit and secure.
Considering that most netizens already concerned about the security of their information, it doesn’t help when they visit a site and are greeted with an SSL error message. If you’re a website owner, error messages can drive your sales down and cause reputational damages to your brand value. It is, therefore, vital that we take steps to resolve these errors in a timely manner and retain the trust of customers.
Secure a Website in Few Clicks – Save Up to 79%
Save 79% on Sectigo SSL Certificates. It includes unlimited server licenses, reissuances, 256-bit encryption, and more.
In this article, we’ll take a look at the NET ERR_CERT_COMMON_NAME_INVALID error and attempt to understand why browsers flash this warning message.
Let’s get started by discussing the ERR_CERT_COMMON_NAME_INVALID chrome fix.
How to Fix the NET ERR_CERT_COMMON_NAME_INVALID Error in Chrome
The common name on your SSL certificate refers to the domain name for which the certificate was issued. For example, if you have a site www.mywebpage.com for which you’d like an SSL/TLS certificate, then the common name you would enter while filling out the certificate signing request (CSR) is mywebpage.com.
The browser displays the “NET ERR_CERT_COMMON_NAME_INVALID” warning when the name on the SSL certificate does not match the one in the address bar, or if there is a Chrome browser error. A common name mismatch happens if the domain on which the SSL certificate is installed is not listed on the certificate (either as a common name or subject alternative name [SAN], or covered under a wildcard). Additionally, a misconfigured redirect could also be a potential trigger.
To troubleshoot this error, we’ll have to try a few different methods to identify and fix the issue. Before we begin, make sure that the date, time, region settings are set up correctly. If they aren’t, they can create issues of their own.
Next, let’s look at fixing the error from the point of view of a website owner. We’ll later discuss how to fix the NET ERR_CERT_COMMON_NAME_INVALID error code from the perspective of a site visitor.
1. Does the Domain Have the Correct Certificate Installed?
The most common reason for the error is a mismatch between the certificate and the domain name. Check if the cert secures the domain on which it’s installed. You can achieve this by inspecting the content of the certificate and comparing the domain on which the certificate is installed to the “Issued to” information (or the list of SANs on the SSL cert. Or, in case of wildcard certs, if the domain is covered by a wildcard).
2. Check for Misconfigured Redirects
Does your browser forcefully redirect visitors to another version of your website? Or does it force traffic over a www or a non-www connection? Note that not all SSL/TLS certificates secure both www and non-www versions of a website, so you’ll need to check that your current SSL cert is covering the version your site defaults to. Depending on the scenario, you may want to reconfigure your settings. Either you can eliminate the redirect or, if the redirect is necessary, you might need to obtain another certificate that covers the domain to which your traffic is being diverted.
3. Ensure Your WordPress and cPanel Settings Are Configured Correctly
For any site to be available over a secure HTTPS connection, you will need to have an SSL certificate installed. If you have a WordPress site, changing the site’s protocol from HTTP to HTTPS will not automatically make your website available over a secure channel.
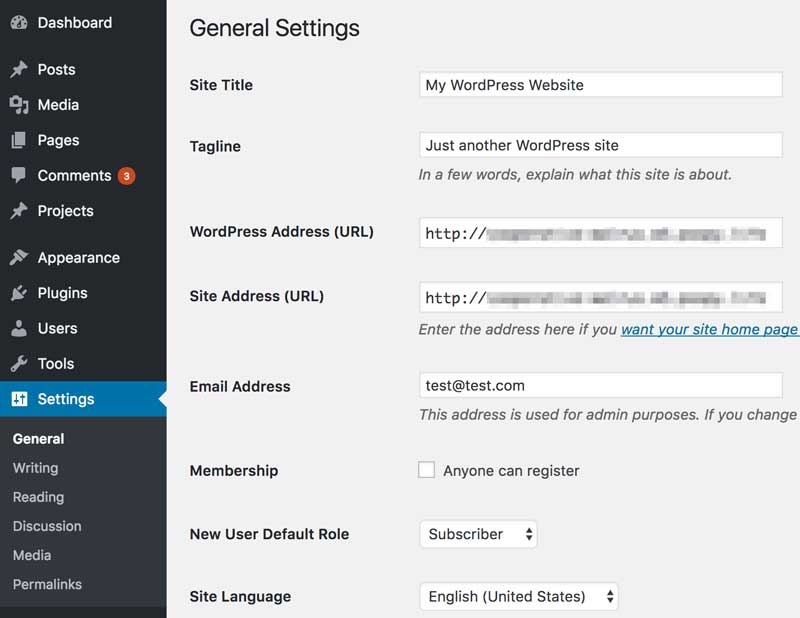
However, it can cause browsers to display the “NET ERR_CERT_COMMON_NAME_INVALID” warning. Revert the address to the old one, by editing your account’s general settings, to get rid of the error message in the interim before you purchase an SSL cert.
Once you’ve made the changes in WordPress, navigate to phpMyAdmin in your cPanel dashboard and select the database for your relevant website.
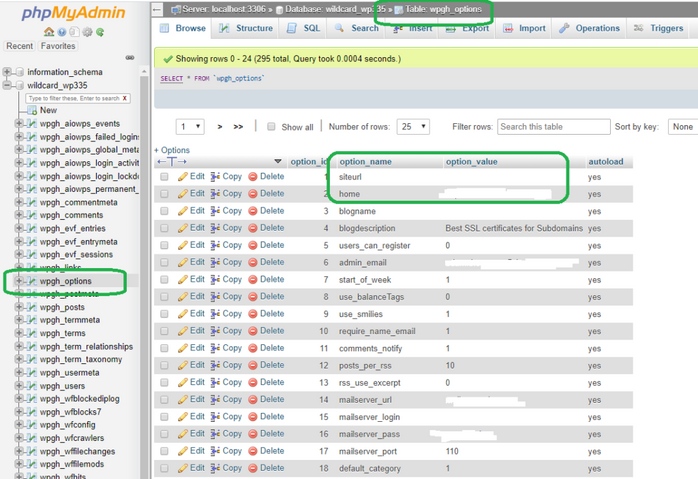
Select the wp_options and edit the site URL and home URL and ensure they have identical web addresses.
Now, let’s dive into the troubleshooting steps you can perform if you’re a website user:
1. Are Chrome Plugins or Browser Extensions Responsible for the Error?
First and foremost, we need to identify the reason the error message is showing up. Once we have that figured out, we can apply the fix accordingly. Try accessing the website through the browser’s incognito mode. If you don’t encounter any error codes, and everything runs smoothly in private browsing mode, chances are one of your browser extensions are creating the problem. Head over to chrome://extensions/ and activate each one individually and access the website. Once you find the plugin that’s causing the error, you can remove or disable it.
2. Clear Your Cache
Corrupted cache or cookies can sometimes cause such error messages to appear in Chrome. To clear the cache, press the CTRL+SHIFT+Del keys on the keyboard and see whether this resolves the issue.
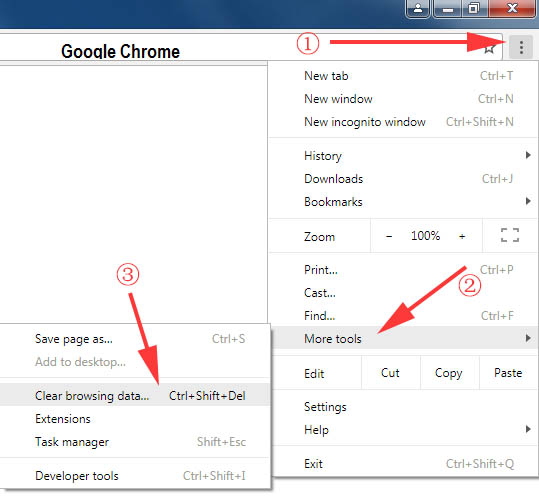
You can also try clearing the SSL state.
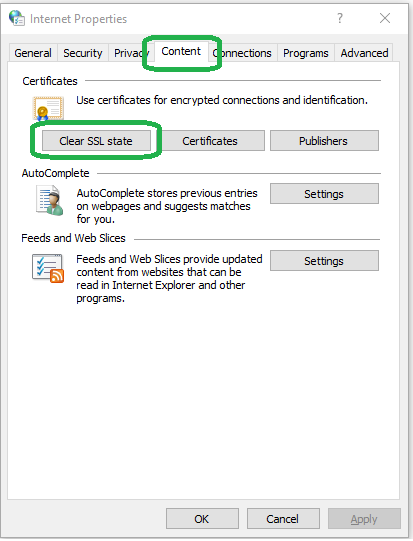
From the start menu, type inetcpl.cpl. A dialog box named Internet Properties should open up. Go to the content tab and select Clear SSL State.
3. Check Your Proxy Settings
Your proxy settings determine how your web traffic is routed. Any misconfigurations in your proxy settings can restrict your access to the web and can cause your browser to display a variety of warning messages.
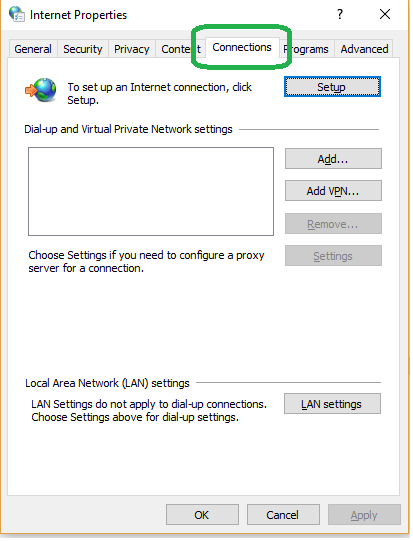
Under Internet Properties (you can access it as described in the previous step), go to the Connections tab.
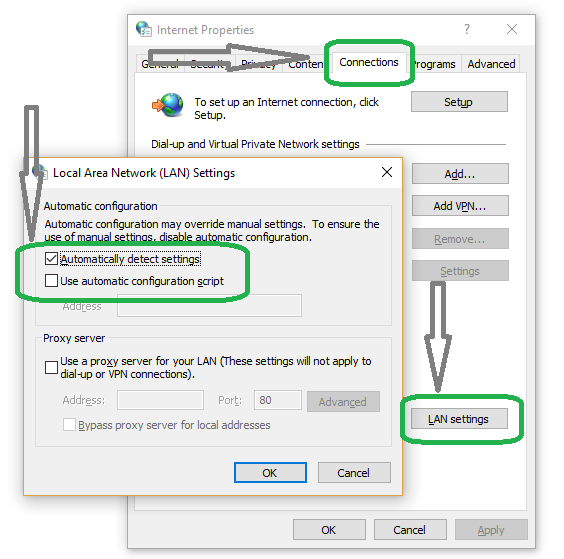
Click on LAN settings and check the Automatically detect settings box. Uncheck other options and click OK.
4. Update Your OS and Browser
Outdated applications can have a host of security and compatibility bugs that can be sources of endless troubles. Double-check that you installed the latest updates for your operating system as well as the Chrome browser.
As a last resort, you can enable HTTPS scanning in your antivirus or temporarily turn off your antivirus or firewall since these can sometimes block connections. However, it is never a recommended practice to disable your firewall or to disable SSL warnings, but these fixes might temporarily let you access the website. They also leave you at great risk of falling victim to a multitude of cyber threats.