We’ll break down the differences between a digital certificate vs signature and how each plays a role in cybersecurity
If you’re not sure how to recognize a digital signature vs a digital certificate, then don’t worry, you’re in the right place. The digital signature and digital certificate are both the fundamental concepts within the realm of cybersecurity.
There is a fundamental difference between a digital certificate vs. a signature. Digital certificates are all X.509 certificates that are issued by one or more publicly trusted certificate authorities (CAs). On the other hand, a digital signature is a unique numeric string that identifies the signatory. However, they both help each other. For example, a publicly trusted digital certificate is signed with a trusted CA’s digital signature, and a digital signature is possible, in part, because of a digital certificate.
Still confused? No worires. In this article, we’ll explain everything about the digital signature vs digital certificate and how they are used in the real life to secure and authenticate emails, software, and websites.
What’s the Difference Between a Digital Signature and a Digital Certificate?
Digital Certificates
In general, the term digital certificate describes all X.509 certificates. It’s a list that includes an SSL/TLS certificates, email signing certificates, code signing certificates, device certificates, and document signing certificates. Here’s an example of an SSL/TLS certificate (i.e, a website security certificate or server certificate):
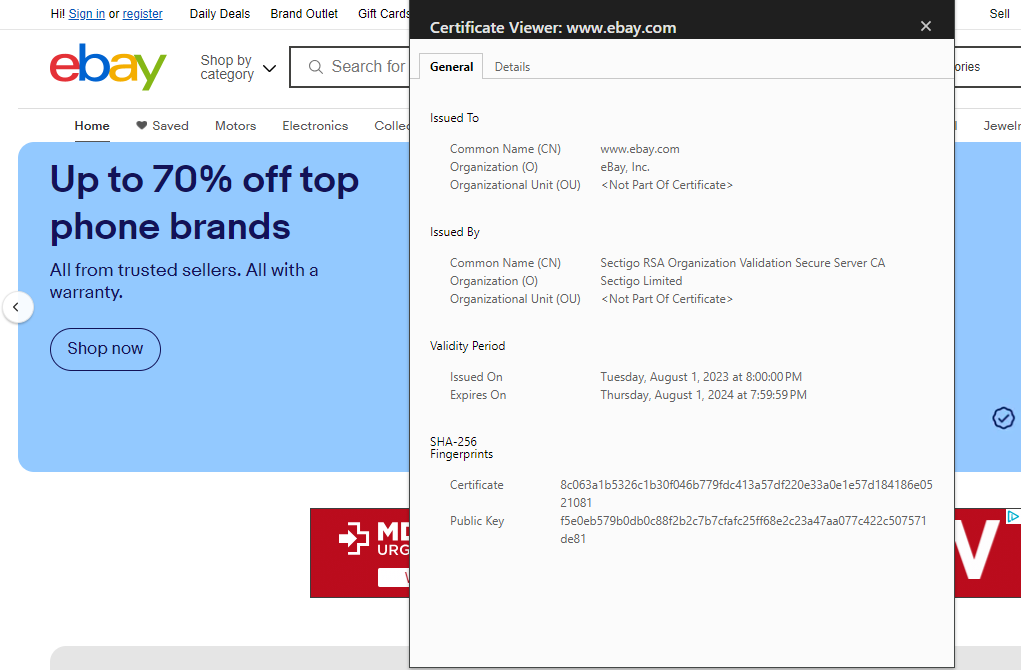
Depending on your needs, you may need a client authentication certificate in one instance and need a new website certificate in another. Regardless of which type of certificate you choose, it must be digitally signed by a publicly trusted certificate authority (CA) for browsers, email clients, and Windows operating systems to trust it.
Digital Signatures
A digital signature is a unique numeric string of identifying data that can be affixed to a digital asset; it validates the signer’s identity online. It’s a type of electronic signature that serves a different purpose than traditional electronic signatures.
- A digital signature provides authenticity and verified identity over the insecure Internet.
- An electronic signature is primarily a digital representation of a handwritten signature.
Using a digital signature is akin to the digital equivalent of having a notary sign and stamp documents for you, so that someone who has never seen or met you can trust that it’s legitimate. Here’s what an email digital signature looks like:
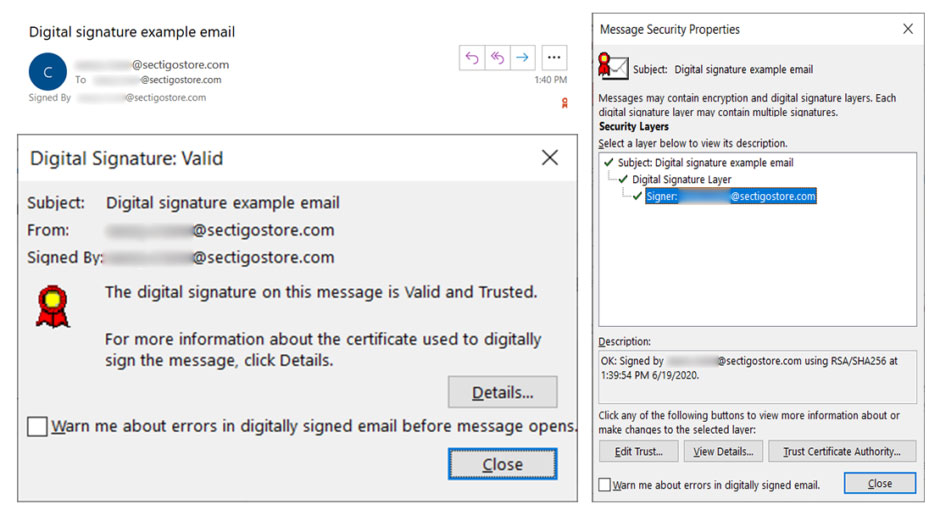
Taking a Closer Look at Digital Signatures vs Digital Certificates
When we talk about comparing a digital signature vs a digital certificate, we first need to understand that they’re both intertwined. Much like how your bank check can’t be used until you sign it, you need a digital signature to authenticate to do certain things online.
Likewise, just as you need a check to sign that displays your official account and bank routing information to complete a financial transaction, you also need a digital certificate to accomplish certain tasks. (You can’t just sign any ol’ piece of paper and use it as a bank check, obviously!)
Let’s do a side-by-side comparison of these two digital assets to understand their individual roles in digital trust.
| Features | Digital Signature | Digital Certificate |
| Definition | A digital signature is a cryptographic visual marker that provides non-repudiation and validates the authenticity and integrity of digital documents, connections, messages, and other data. | A digital certificate is a small file that verifies the identity of a person, device, or organization on the internet. It contains information such as the entity’s name, public key, expiration date, and digital signature of the certificate authority. |
| Purpose | Verifies the legitimacy and reliability of digital documents, ensuring that the sender can’t deny sending the message and that the message content hasn’t been altered since it was signed. | Ties your organization’s verified digital identity and public-private key pair to various types of digital assets (email, software or code, websites, etc.) |
| How It’s Created | The signer hashes their email, document, or file and then encrypts the resulting hash digest using their cryptographic key to create the digital signature | In the case of publicly trusted digital certificates, a third-party certificate authority (CA) issues the certificate after conducting a thorough vetting of the applicant’s digital identity. This whole process begins with a certificate signing request (CSR). |
| Scope of Application | Commonly used for signing emails, Microsoft Office documents and PDFs, software, code, and other digital data to guarantee its authenticity and integrity. | Depending on the type of certificate, it – ensures secure connections and communications between parties; – establishes trust through authentication; – enables encryption of data during transmission. |
| Use Cases | Widely used in various sectors, including legal, financial, software development, and government, wherever file authenticity and integrity are critical. | Primarily used for securing internet communications (email and websites) and providing authentication for online services. |
| Verification Procedure | The recipient uses the sender’s public key to decrypt the digital signature and verify it by comparing it to a new hash of the document. If both hashes match, the signature is valid. | The recipient validates the certificate using the CA’s public key to ensure its authenticity and verify the sender’s identity. The certificate’s origins can be traced through its certificate trust chain. |
| Compliance and Legal | Digital signatures are accepted in various countries, each with its own set of governing laws. For example, the U.S. relies on the E-SIGN Act, while EU member states use the eIDAS Regulation. Familiarity with local regulations is important when using digital signatures. | Digital certificates, issued by accredited CAs, are widely accepted for online transactions and communications. They confirm the identities of one or both parties taking part in the transaction, thereby adding a layer of security and trust to online commerce. |
Let’s understand how digital certificates and digital signatures work with various types of technology.
Digital Signature vs Digital Certificate: Email Signing Certificate
An email digital signature certificate, also known as email signing certificate or S/MIME certificate, is a digital certificate that organizations use to boost email security. Much like other X.509 digital certificates, it relies on the principles of public key infrastructure (PKI) to encrypt and decrypt the emails. This provides end-to-end encryption, which enables your email information to remain secure both while it’s at rest and in transit.
When a user installs an S/MIME certificate on their email client, they get the ability to embed their digital signature on the emails. The recipients will see a small ribbon icon in the email. When they click on the icon, it will show the sender’s name, email address, and original email subject. The digital signature provides assurance of the sender’s identity.
When the user sends an email, the email contents, along with the digital signature, get hashed, and the hash value is encrypted. What it means is that if anyone tries to tamper with the email contents or the digital signature while the email is in transit or at rest, the hash value changes, and the recipients would instantly know about it. This helps to protect the integrity of the email.
Get a Sectigo Brand Email Signing Certificate Starting as Low as $14.95/year!
Save 15% on Secure Email Certificates! Get the lowest prices on trusted email certificates from Sectigo.
Shop NowDigital Signature vs Digital Certificate: Code Signing Certificate
A code signing certificate is a digital file that protects downloadable software, device drivers, applications, executables, and scripts.
A code-signing certificate allows a developer or publisher to put a unique digital signature on the piece of software they develop using their private keys. This digital signature, along with the entire content of the software, gets hashed. No one can replicate, alter, or delete this digital signature when the software is in transit. If the digital signature or the content of the software is modified in any way, the hash value changes and the user receives a security warning.
When a user tries to download software from the internet, a Windows SmartScreen security warning box pops up. If the software is signed using a code signing certificate, it will show the software publisher’s name as a “verified issuer.” If not, the publisher’s name would be shown as “unknown” or “unverified.”
Get a Sectigo Code Signing Certificate For As Little As $219.45/Year!
Save up to 42% on Code Signing Certificates! Get the lowest prices on trusted certificates from Sectigo.
Shop NowDigital Signature vs Digital Certificate: SSL/TLS Certificates
An SSL certificate (or, more accurately, a TLS certificate) protects the data transmission between a website and a browser by creating a secure, encrypted communication channel. Much like other X.509 digital certificates, an SSL/TLS certificate also needs a digital signature. It can be signed by the publicly verified certificate authority (what’s known as a CA signed certificate) or the users themselves (aka a self-signed certificate), although the latter isn’t publicly trusted.
So, how does this work? After a user purchases an SSL certificate, they send an unsigned certificate via a certificate signing request (CSR) to the certificate authority. The CA verifies the information provided in the CSR as well as the applicant’s domain ownership. After the successful validation process, the CA inserts its digital signature using its intermediate root certificate’s private keys.
All the browsers have a root store in which the CA’s trusted root and intermediate root certificates are pre-downloaded. When a user tries to open a website, the browser verifies the CA’s digital signature by using this root store. If it can’t find the matching root CA (or chain of certificates) in its root store, the browser will display an error page “your connection is not private.”
Get a Sectigo Brand SSL/TLS Certificate Starting at $8.78/Year!
Save 85% on SSL Security Certificates! Get the lowest prices on trusted SSL certificates from Sectigo.
Shop NowFinal Thoughts
We hope you have found this article useful for understanding the difference between a digital signature vs a digital certificate. The main takeaway here is that you need to buy a digital certificate, which will enable you or your CA to insert a digital signature, to protect your software, digital connections, and correspondences.
If you get your digital certificate from SectigoStore.com, you will get up to an 80% discount on the retail price, 30-days money back guarantee, 24/7 live customer support, and much more!
Wildcard SSL Certificate Price Comparison
 (9 votes, average: 4.56 out of 5)
(9 votes, average: 4.56 out of 5)