Would you walk into a store that looks like a front for some illegal business? Probably not, at least hopefully not. Welcome to the 21st century, where websites are the virtual storefronts. Most security-aware netizens won’t visit a website if it comes with ‘Not Secure’ written all over in red. Unless you are a cybercriminal (or a terrible businessman), your target audience is probably broader than gullible users, who ignore security warnings and waltz into your website. It is, therefore, in the best interest of users as well as website owners to use a trusted SSL certificate and fix any certificate errors for a secure and smooth browsing experience.
SSL Certificate Problem
There are a few different issues that can result in SSL certificate issues. If you are facing any kind of SSL certificate issue, you have come to the right place. This article will talk about all the issues and, more importantly, how to solve them so that your website is ready for its visitors.
Various SSL certificate problems or SSL certificate errors can occur that include SSL certificate not trusted, client server error, SSL certificate mismatch error, or invalid server certificate error. Some of these SSL certificate problems are due to technical glitches that can be tackled with a little help.
What Is SSL/TLS? Why Do We Use an SSL/TLS Certificate?
SSL or Secure Sockets Layer and TLS (Transport Layer Security) are cryptographic protocols designed to provide a secure communication channel between clients and servers over the internet. SSL is the older encryption protocol whereas TLS is the relatively newer version. The intention behind having an SSL/TLS certificate was not just for authentication but also to establish the identity of the remote server with whom the client browser communicates. For example, consider your browser is talking to https://www.yourdomain.com, and the SSL/TLS certificate for the website is valid. This indicates two things:
- The channel is encrypted; hence, anyone eavesdropping over the network will end up with garbled information that can’t be read.
- Your browser is talking to the actual server and not an imposter.
That, of course, was the intention. Fast-forward to reality, and we now have around 50% phishing websites using an HTTPS connection to spam users. It is only with an EV SSL certificate that a domain is supposed to get thoroughly vetted in terms of its identity . At the very least there is accountability since the business needs to be registered and the owner needs to pay for the EV certificate.
SSL/TLS provides data confidentiality and data integrity. We use SSL /TLS protocol to ensure that data travels securely over the wire. Encrypting data in transit helps to prevent any malicious user from sniffing the network to steal sensitive information like passwords, credit card details, etc.
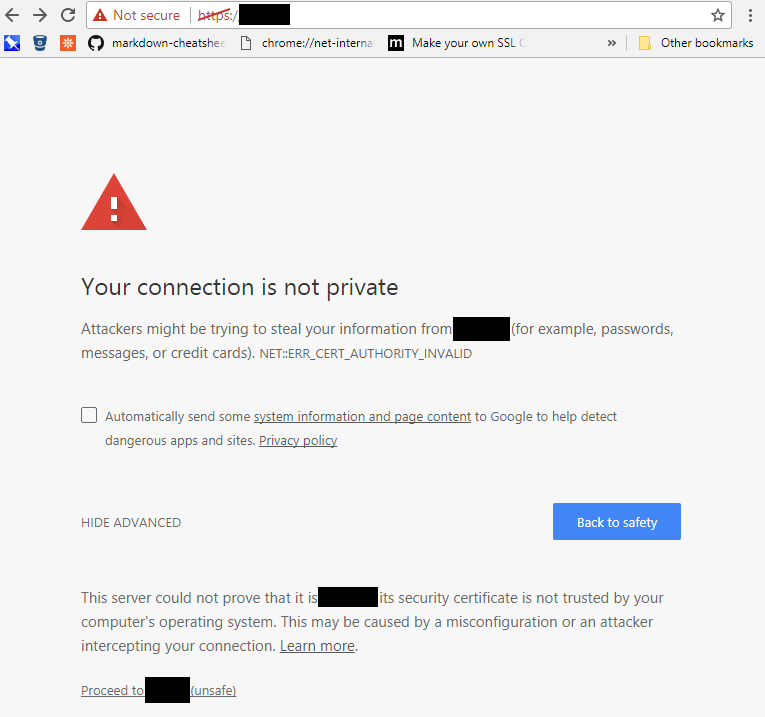
SSL/TLS certificates are signed by a third party, called Certificate Authority, which prevents the attacker from creating a fake certificate and passing it off as a legitimate one. The browser warns the user if the website uses an invalid certificate (it can’t trace back to the root CA, or there is a mismatch in the names enlisted in the certificate). It is recommended not to proceed to such a site since it could indicate that you are being directed to a phishing or a fake website.
What Does It Mean to Have an Invalid SSL Certificate?
- The user’s visiting your website will lose trust due to a lack of perceivable credibility.
- Some users might be convinced that you are hosting a malicious website and would choose to steer clear even after the issue gets fixed.
- Adversely impacts business and brings down the reputation especially if you are not a known player experiencing a temporary technical glitch.
For the end-user:
- If the SSL certificate gets flagged as invalid by the browser, the data exchanged between you and the website you’re trying to connect to will be transferred in cleartext. Potentially, any user credentials or other sensitive data communicated over the channel can be sniffed or stolen. It is always recommended not to proceed over an insecure connection.
- Apart from the risk of sending data unencrypted, there is a good chance that the site you are trying to connect to could be designed to phish your credentials or with other such malicious intent. Arguably, having a trusted SSL certificate does not in any way ensure that such attacks don’t happen. You can, at the very least, always verify the certificate issuer information by viewing the certificate details.
Reasons for the Error and How to Fix It
There can be a few reasons why the browser decides to flash the invalid SSL certificate error message on our screens. Below, we take a look at some of these and explore ways to fix them.
- If the website owner misconfigures the SSL certificate during installation, there is no way to access the HTTPS version correctly. Every time someone accesses the website, their browser will flash this error on the screen.
- Invalid SSL certificate / Intermediate certificates error could occur when as a website owner, you are trying to install the certificate on your web server or CDN, but the relevant certificate details are not filled correctly. You can use the free SSL Checker from Qualys SSL Labs to check if the SSL certificate has been configured correctly on the web server.
- The certificate has been revoked or was obtained illegally.
- ERR_CERT_COMMON_NAME_INVALID error indicates there is a possible mismatch in names of the domain you are trying to access and the one included in the certificate. The website owner must confirm the web address in the correct format before the CA issues the certificate. Remember that the domain https://www.example.com might be included in the certificate while https://example.com is different and might not be registered as a part of the SSL certificate.
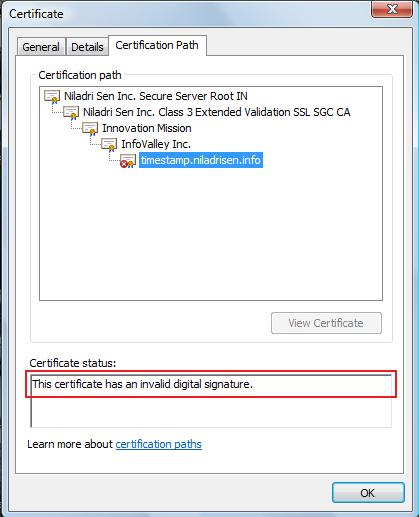
- The certificate’s chain of trust is broken (could be because the root CA can’t be verified, or the root/intermediate certificate has expired).
- The certificate must be renewed before the expiry of the certificate to avoid any conflict arising out of time violation. Ensure that the date/time is set correctly on your computer since that might be used to assess the validity period of the SSL certificate of the website.
- The certificate structure is broken, or the certificate’s signature can’t be checked.
- It is preferred to obtain a certificate from trusted Certificate Authorities (CA) like Symantec, Thawte, Comodo, etc. to avoid any security warnings from browsers. If a self-signed certificate is being used, configure the domain to use Full SSL instead of Full SSL (Strict).
- Check the antivirus or firewall. You might need to disable any option like “encrypted/SSL scanning or checking.”
- Websites using only SHA-1 encryption are flagged as insecure and need to update their security certificates.
Invalid SSL/TLS Certificate – Security implications
Since an invalid SSL/TLS certificate renders the communication channel between client and server unencrypted and data travels in cleartext, this could lead to a serious breach in security. An attacker listening on the network can sniff the user credentials and session ID for the particular session and use the information gleaned to impersonate a legitimate user or exploit weaknesses in session management. An invalid SSL certificate can also be indicative of a malicious website. When in doubt it is always recommended to not proceed to sites which have been flagged as insecure or display security warnings.
As a website owner, the brand reputation gets impacted if on visiting your website, the end-user is greeted by a plethora of security warnings or error messages. It is advisable to purchase an SSL/TLS certificate from a trusted CA, especially since they are affordable, and the benefits far outweigh the costs. Read more about SSL vs TLS aspects on our SSL resources.
Encryption Resources
- Hashing vs Encryption — The Big Players of the Cyber Security World
- What Is Encryption and How Does It Work?
- Symmetric vs Asymmetric Encryption – 5 Things You Should Know
- SSL vs TLS: Decoding the Difference Between SSL and TLS
- What Is Asymmetric Encryption & How Does It Work?

 (39 votes, average: 4.31 out of 5)
(39 votes, average: 4.31 out of 5)