If you’re a website owner who’s been worrying endlessly about encryption strengths and whether to opt for a 128 bit encryption or 256-bit encryption, you’ve just got to read on to ease your nerves! For our other tech-savvy readers, concerned about accessing insecure websites, we’ll look at if a 128 bit SSL encryption standard can be adopted with reasonable safety.
PositiveSSL EV Certificates from $79.84/year!
Get the lowest prices on trusted SSL/TLS certificates from Sectigo brands.
Shop for Sectigo SSL CertificatesWhen it comes to choosing the right encryption strength in terms of a digital certificate, most sellers offer up to 256-bit encryption. Still, the actual encryption level that’s utilized to secure your data depends on a bunch of other factors.
Let’s take a look at how encryption comes into play as you surf the internet, shop on Amazon, or engage in other financial transactions.
What Is 128 Bit AES
A 128 bit advanced encryption system (AES) is a technique of encrypting sensitive data using session key that is 128 bit long. This national security agency (NSA) approved encryption protocol uses symmetric encryption to convert plain text into encrypted text by using ten transformation rounds.
What Happens Behind the Scenes When You Access a Website
Every time your web browser (Chrome, Firefox, etc.) talks to the server where the website is hosted, a three-way handshake occurs in the background followed by an SSL handshake if you’re trying to access the site over HTTPS.
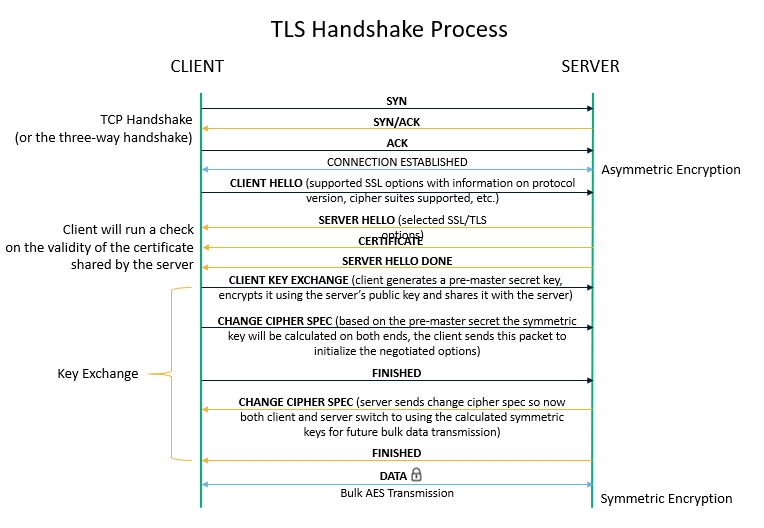
Without getting into the details of how an SSL/TLS handshake works (that’s another topic for another day), in the image above, we can see some form of negotiation happening between the server and the client where they tell one another the standards and protocols supported on each end. These negotiations determine the best possible standards and protocols to use. Then, once that’s decided, we proceed with bulk data transfer.
In simple terms, even if you were to choose a certificate that supports up to 256-bit encryption, the outcome is dependent on these negotiations and the default server configurations. For all you know, you could end up with 128 bit encryption or significantly less encryption strength if the server you’re connecting to still supports outdated ciphers and its configuration settings have not been updated, or if your browser has not been updated.
This means that it’s better to choose a 256 bit encryption certificate and check your server configuration settings — as well as you browser — to ensure they both support it.
Do I Have 128 Bit Encryption & How Do I Know
A 128 bit encryption describes the length of the key (128 bit) to encrypt the data transferred on an untrusted network. 128 bit encryption is used in encryption protocols including AES and SSL/TLS. Although 128 bit encryption is not yet obsolete, a more secure 256 bit encryption is widely used in modern protocols.
If you don’t know if you have 128 bit encryption or 256 bit encryption, you can check it on your SSL certificate. You can click on the padlock icon on your website and click on “Certificate (Valid)”. Go to the “Details” section and check your “Signature Algorithm”. It describes the length of the key used to encrypt your online conversation. If you have sha128RSA, it means you have 128 bit encryption.
How Secure Is 128 Bit Encryption
If you are brooding, “How secure is 128 bit encryption?”, the sincere answer is it is very secure.
A 128 bit encryption has 2128 combinations of keys if a criminal uses a brute force attack. On the other hand, a 256 bit encryption is many times more secure than 128 bit encryption. A 256 bit encryption has 2128 more keys than 128 bit encryption.
So, What’s 128 Bit Encryption Mean Anyway?
When we talk about 128 bit encryption, the “128” refers to the length of the key that’s used to encrypt your data. What this really means is that to crack the encryption key, an attack would need to brute-force up to 2128 possible combinations to decrypt your data.
Obviously, while 2128 might be a near-impossible number for humans to handle, computers can process information a lot faster. However, it would take approximately 885 quadrillion years for the most powerful supercomputer (as of 2017) to brute force a 128-bit AES key.
Here are a few key size examples and the amount of time it would take to crack each of them:
| Key Size | Time Required to Crack |
|---|---|
| 56-bit | 399 seconds |
| 128-bit | 1.02 x 1018 years |
| 192-bit | 1.872 x 1037 years |
| 256-bit | 3.31 x 1056 years |
128 Bit Vs 256 Bit Encryption
128 bit encryption uses a 128 bit long symmetric key, while a 256 bit encryption uses 256 bit long symmetric key. Mathematically speaking, 256 bit key is 2128 times longer than the 128 bit key, and thus, it’s much more difficult to crack. Therefore, in 128 bit vs. 256 bit encryption, the apparent winner is 256 bit encryption. However, given the present computing rates, 128 bit encryption is also very difficult to crack.
The bottom line here is that while 128 bit SSL encryption will take less time to crack than 256-bit encryption, it’s still reasonably safe to use. Having said that, these are all contingent on AES being implemented correctly, with sufficient entropy, and without falling victim to side-channel attacks, insecure passwords, etc.

 (36 votes, average: 4.89 out of 5)
(36 votes, average: 4.89 out of 5)