What you need to know about digital certificates and how they can improve your web security
The internet has given us so many advantages – the ability to communicate to anyone anywhere, buy anything with the touch of a button, build a new career or business and so much more. However, to take advantage of the internet, we must put our personal information out there – whether that is our home address, personal opinions, credit card information and so on. With that, it is vital we protect this constant stream of personal information that travels through so many different paths. And how do we do this? With digital certificates.
A digital certificate (aka X.509 certificate) accomplishes so much in so many different ways but, at the core, the purpose is generally to protect our information, data or technology.
What is a Digital Certificate – The Short Answer
Technically, digital certificates act as online credentials that utilize public key infrastructure (PKI) and digital encryption keys to authenticate the certificate owner(s) and encrypt communications/data/software.
In simpler terms, digital certificates protect websites, documents, emails, servers, and other assets against cyber criminals. How do they do that? Let’s dig in…
What is PKI?
As mentioned, PKI is needed for digital certificates to work. As the name says, it is the digital infrastructure that enables digital certificates to do what they do.
What is PKI? For the answer to that question, check out our article “What Is PKI? A Layman’s Guide to Public Key Infrastructure.”
Now, let’s dive back into digital certificates and what they do.
What Are Digital Certificates Specifically Used For?
We’ve covered what digital certificates generally do, but to understand what they specifically accomplish, you need to know about the most common types of digital certificates. There are many types of digital certificates that serve different security purposes – here are some of the most commonly used and known:
SSL Certificates
Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) certificates create a secure (and encrypted) connection between an at-home computer (the client) and website (web server). This ensures that hackers can not steal data and information from users who interact with a website. It is vital that a website have an SSL certificate. So vital, that a browser will read “not secure” by your URL if you do not have an SSL certificate.
To remove the “not secure” message and replace it with the coveted padlock icon, a web admin must install an SSL certificate.
Code Signing Certificates
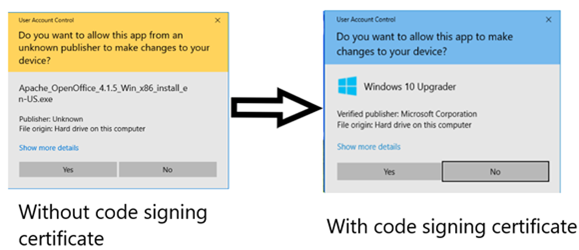
When downloading a software, the last thing you want to see is a warning message. If you get a warning messaging when attempting to download/install/run a software or app, then that most likely means that the developer is not using a code signing certificate. A code signing certificate creates a “digital shrink wrap” over the software.
This certificate tamper-proofs the software code, which preserves the integrity of the content. In addition, this certificate also verifies the identity of the owner, so that the end-user can confirm that they are downloading software from the intended source and not an imposter hacker.
This image shows software without a digital certificate and software with a digital certificate:
Get a Code Signing Certificate for $79/year!
Assert Publisher Identity, Ensure Software Integrity and Avoid Browser and Antivirus Warnings.
Shop NowS/MIME Certificates
Secure/Multipurpose Internet Mail Extensions (S/MIME) certificates, aka personal authentication certificates, are primarily used to digitally sign and encrypt emails. What this does is two things:
- Ensure the email recipient can verify the identity of the email sender through a digital signature.
- Provide end-to-end encryption to ensure the contents of the sent email cannot be tampered with.
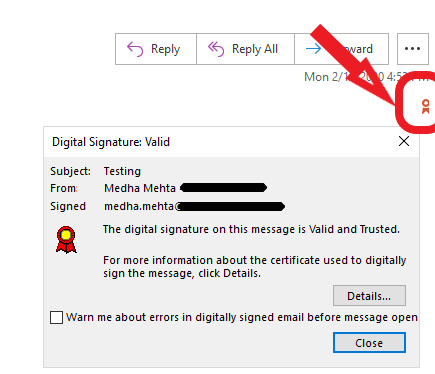
This means that the email sender can have peace of mind that the contents of the email they sent are secure and cannot be deciphered by a hacker AND the email recipient has peace of mind because they can verify that the sender is who they say they are (and not a hacker attempting a phishing attack).
This is what an email signed with a digital certificate looks like:
Get a Sectigo email signing certificate for only $12.95/year!
Save 20% on Secure Email Certificates! Get the lowest prices on trusted email certificates from Sectigo.
Shop NowDocument Signing Certificates
As the name states, a document signing certificate is for a document – they allow you to digitally sign and securely send documents. This is not to be confused with an e-signature. An e-signature is nothing more than a typed name. They do not secure or truly prove anything.
A digital signature with a document signing certificate can be verified because the person who is signing and sending the document is using a private key that is exclusively owned by them to sign the document. In addition to this, the recipient will be notified if a hacker tampered with the document – this also goes a long way in upholding the integrity of the document.
This is what a PDF document signed with a digital certificate looks like:

Final Word
As you see, digital certificates can indeed provide that extra measure of security we need to be able to enjoy all the convenient and exciting things the internet provides.
If you’re looking to enhance the online security of your website/business, and think digital certificates could be the answer – we highly recommend taking a look at SectigoStore.com. With every type of digital certificate you read about here, the best prices on the market and 24/7 customer support to guide you through your web security journey, you are sure to accomplish whatever digital security goals you have!
